
📌 Introduction
Choosing the right database is not just about syntax or speed — it's about choosing the right tool for your architecture, data model, and team culture. PostgreSQL and MongoDB are two heavyweights in the database space, often compared but built on very different ideologies.
In this article, we'll dissect both databases and help you understand when and why to use each in 2025 and beyond.
🧠 Philosophy & Data Models
| Feature | PostgreSQL | MongoDB |
|------------------|----------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|
| Type | Relational (SQL) | NoSQL (Document) |
| Schema | Strict schema with types | Flexible, schema-less |
| Data Format | Tables, rows, columns | JSON-like BSON documents |
| Relations | Foreign keys, joins | Embedding, referencing PostgreSQL: Think spreadsheets with strict rules — perfect for structured, interrelated data.
MongoDB: Think JSON-like collections — ideal for fast-changing or hierarchical data.
⚙️ Performance: Who's Faster?
| Workload Type | PostgreSQL Strength | MongoDB Strength |
|-------------------|---------------------|------------------|
| Complex Queries | ✅ | 🚫 |
| Full-text Search | ✅ (with `tsvector`) | ✅ (built-in) |
| Real-time Ingest | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Aggregations | ✅ (window functions)| ✅ (aggregation pipeline) |PostgreSQL's performance shines in analytical queries with relational integrity. MongoDB wins in high-speed data ingestion and denormalized workloads (like IoT or logs).
💡 Key Differences
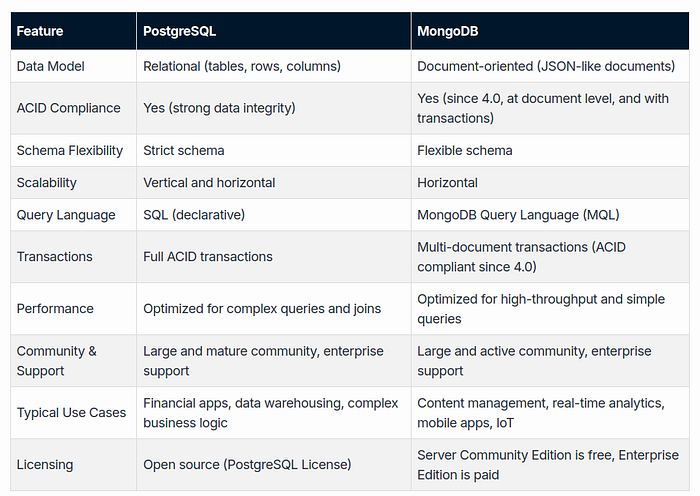
💡 Use Cases
PostgreSQL is best when:
- You need ACID compliance.
- You rely on complex joins, views, or stored procedures.
- Your data model is structured and evolves slowly.
- You're building financial, ERP, HRMS, or inventory systems.
MongoDB is ideal when:
- You want to move fast with rapidly changing schemas.
- You're storing nested, JSON-like documents.
- You're building real-time apps, CMS, or analytics dashboards.
- You're dealing with unstructured data.
🧰 Developer Experience
- PostgreSQL has mature tooling (e.g., pgAdmin, DBeaver) and strong standards (SQL).
- MongoDB has Atlas, Mongo Compass, and great driver support in most languages.
In 2025, MongoDB continues to dominate in developer agility, while Postgres leads with its mature ecosystem and stability.
🔒 Security & Transactions
FeaturePostgreSQLMongoDBACID TransactionsFull supportMulti-document since v4.0Schema EnforcementYesOptional (via validation rules)AuthenticationRole-basedRole-based, Atlas integrationsEncryptionBuilt-in TLS, TDEBuilt-in TLS, client-side options
PostgreSQL is still the preferred choice for strict, regulated environments.
🔄 Scaling and Replication
- MongoDB offers horizontal scaling via sharding out-of-the-box.
- PostgreSQL prefers vertical scaling, though modern solutions like Citus (from Microsoft) enable horizontal scaling.
If your app needs global scalability, MongoDB gives you easier scaling options.
🧮 Query Language
- PostgreSQL: Uses standard SQL, widely understood and portable.
- MongoDB: Uses Mongo Query Language (MQL) — JSON-like and intuitive but custom.
Both languages are powerful, but SQL gives Postgres an edge in portability and legacy integration.
🌍 Community & Ecosystem
- PostgreSQL: Open-source since 1996, community-driven, stable.
- MongoDB: Open-source core with enterprise extensions, backed by MongoDB Inc.
MongoDB's Atlas cloud offering is a game-changer for startups and enterprises alike.
🚀 Final Verdict: When to Choose What?
| Criteria | Go with PostgreSQL | Go with MongoDB |
|-----------------------------|------------------------------|----------------------------------|
| Need strong data integrity | ✅ | 🚫 |
| Need rapid prototyping | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Real-time analytics | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Complex transactional apps | ✅ | 🚫 |
| Schema-less data | 🚫 | ✅ |
| Time-series/IoT | 🚫 (extensions exist) | ✅ (native time-series support) |✍️ Conclusion
The choice between PostgreSQL and MongoDB is not binary — it's contextual.
- If your data is structured, relational, and predictable, PostgreSQL will reward you with power, reliability, and maturity.
- If your data is flexible, nested, and fast-changing, MongoDB will enable rapid development and scale.
In modern architectures, it's not uncommon to use both, each serving different parts of the system — PostgreSQL for transactional core and MongoDB for real-time analytics.