Attention mechanism have revolutionized natural language processing (NLP), allowing neural networks to focus on the most relevant parts of input data. But don't worry; you won't need a PhD to understand the basics! This post provides a simplified, educational breakdown of how attention works, focusing on clarity rather than real-world implementation. So, just pay "attention" and let's dive in with a simple code example inspired by the groundbreaking paper, "Attention is All You Need".
Imagine reading the sentence, "The cat sat on the mat." Humans instantly understand relationships between words, like "cat" as the subject and "sat" as the verb. Attention mechanisms enable machines to capture similar relationships, helping them focus on specific parts of input data.
At its core, attention is a function that calculates the relevance of different input parts to a specific query. This relevance is represented as weights, which then create a weighted sum of the input values, highlighting the most important information.
A Simple Analogy
Think of attention as a spotlight. When you spotlight a stage, you focus on a specific area, bringing it to the forefront. Similarly, attention in neural networks highlights specific input parts, making them more prominent for the model's understanding.
Scaled Dot-Product Attention: The Workhorse of Transformers
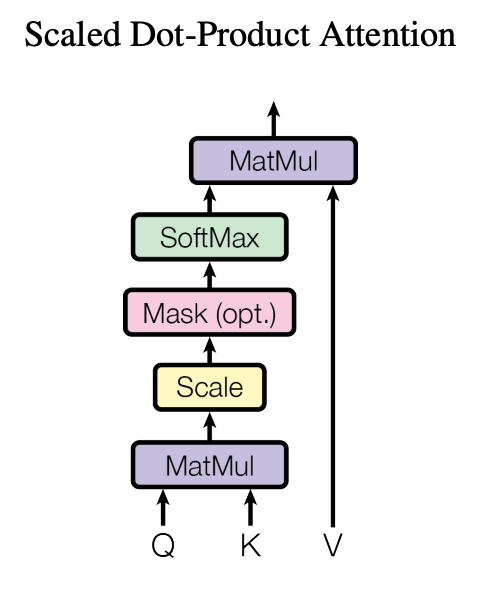
Figure 2: Scaled Dot-Product Attention. (Multi-Head Attention consists of several attention layers running in parallel.)
One of the most popular attention mechanisms is scaled dot-product attention, widely used in Transformer models. Let's break it down:
- Query (Q), Key (K), and Value (V): These matrices are transformations of the input data and represent different aspects of the information being processed. In practice, Q, K, and V are learned parameters in neural networks, adapting to capture context relationships.
- Dot Products: The query is multiplied with each key, generating scores that reflect their similarity. Higher scores mean higher relevance.
- Scaling: These scores are scaled down to prevent the softmax function from producing extreme probabilities, which could destabilize training (imagine trying to train with values that are too big — it's no fun).
- Softmax: The scaled scores are passed through a softmax function, producing attention weights that form a probability distribution (i.e., they sum to one). These weights indicate the relevance of each word to the others.
- Weighted Sum: Finally, the values are multiplied by their respective attention weights and summed, creating an output that emphasizes the most relevant information.
Example Implementation of Attention Mechanism from Scratch!
Let's dive into a hands-on example that implements attention from scratch using Python and NumPy.
Step 1: Initial Word Embeddings
import numpy as np
word_embeddings = {
'she': np.array([0.2, 0.9, 0.1, 0.5]),
'likes': np.array([0.8, 0.3, 0.7, 0.2]),
'coffee': np.array([0.4, 0.6, 0.3, 0.9])
}Word embeddings are vector representations of words that encode semantic meaning. Here, we define embeddings for three words, each in a 4-dimensional space. These vectors are set manually to illustrate the concept. In practical applications, embeddings typically come from an embedding layer trained on large datasets, not manual setup.
Step 2: Create Input Matrix X
We stack the embeddings vertically to form the input matrix X. This matrix will be used to calculate the Query (Q), Key (K), and Value (V) matrices in subsequent steps.
X = np.vstack([word_embeddings['she'],
word_embeddings['likes'],
word_embeddings['coffee']])Note: In real applications, this matrix is generated as part of a larger data preprocessing pipeline.
Step 3: Define Weight Matrices W_q, W_k, and W_v
These matrices are used to compute the Q, K, and V matrices through multiplication. Think of them as the translators that adapt our embeddings for attention. In production models, these weights are learned by the model. Here, they're set manually to illustrate how the transformation works.
W_q = np.array([[0.9, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.9, 0.1, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.9, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.9]])
W_k = np.array([[0.9, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.9, 0.1, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.9, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.9]])
W_v = np.array([[0.8, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1],
[0.2, 0.8, 0.2, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.2, 0.8, 0.1],
[0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.9]])Step 4: Compute Q, K, and V Matrices
These matrices are derived by multiplying X with each weight matrix. In a real neural network, these transformations help the model understand context.
Q = np.dot(X, W_q)
K = np.dot(X, W_k)
V = np.dot(X, W_v)Step 5: Calculate Raw Attention Scores
The dot product of Q and the transpose of K yields the raw attention scores, measuring the relevance of each word to the others.
scores = np.dot(Q, K.T)Step 6: Scale the Scores
To avoid excessively large values that could destabilize training, we scale the scores by dividing by the square root of d_k (the dimension of the key vectors).
d_k = K.shape[1]
scaled_scores = scores / np.sqrt(d_k)Step 7: Apply Softmax to Obtain Attention Weights
Applying the softmax function to the scaled scores converts them into a probability distribution, highlighting the relative importance of each word.
exp_scores = np.exp(scaled_scores)
attention_weights = exp_scores / exp_scores.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)Step 8: Calculate the Final Output
The final output is computed by multiplying attention_weights by V. This output combines the information from the entire sequence in a way that considers the relevance of each word.
output = np.dot(attention_weights, V)Now you've got your attention-weighted output, packed with context-relevant information! Just like a well-focused conversation, the output here only pays "attention" to the most important parts.
Visualizing Attention Weights
Visualizing these weights with a heatmap can show how each word attends to the others, which can reveal insights into what the model "thinks" is relevant. This is particularly useful when analyzing text data!
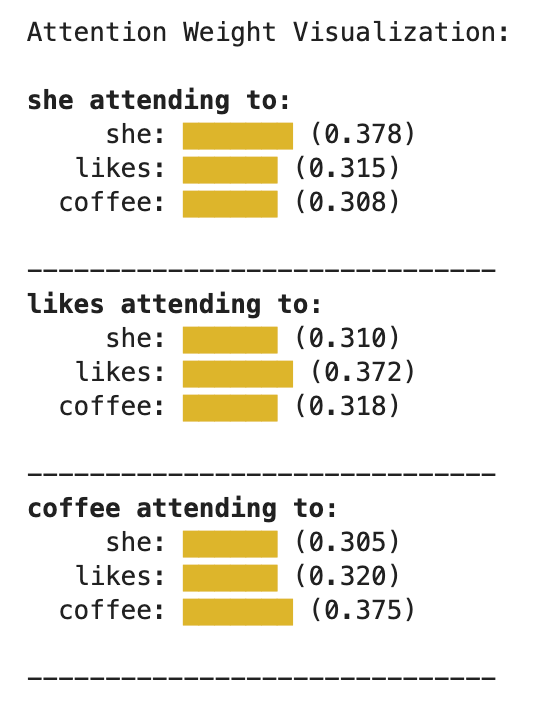
Beyond Words: Attention in Images, Audio, and More
Attention mechanisms have applications far beyond text. In image processing, attention can help models focus on specific regions, and in audio, it highlights important sections of a signal. It's become an essential part of modern neural networks, helping models achieve impressive results across many fields.
Attention has proven essential for advancements in artificial intelligence, allowing models to process information effectively and efficiently. And if you're interested in taking your knowledge further, just stay tuned!
Code:
https://github.com/christoschr97/the-beginner-pytorch/blob/main/attention/Attention_mechanism.ipynb
What's Next? Multi-Head Attention!
In the next post, we'll explore multi-head attention — the big sibling of the single-head attention we just covered. It takes things to the next level by running multiple attention mechanisms in parallel to capture different aspects of input information. Get ready to see attention get bigger, better, and more powerful!
