Data manipulation, analysis, and computation in Power BI are all made possible by the DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) tools. You may conduct intricate computations, transformations, and aggregations on your data with DAX functions, which can be used to provide insightful insights, visuals, and reports. We'll look at some of the Power BI DAX functions that are most often used, what they do, and how to use them.
Check out the mind map for list of functions:
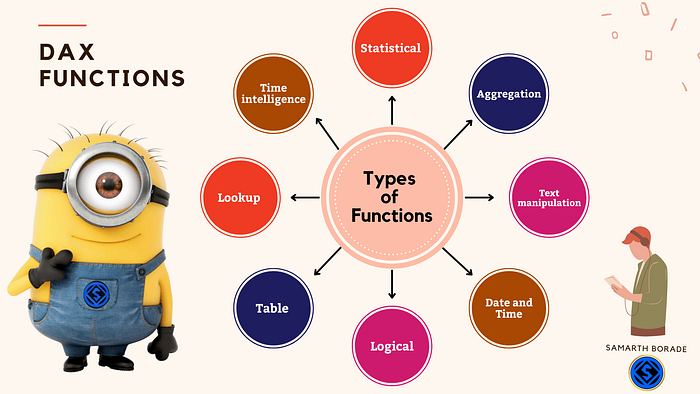
1. Aggregation functions: SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MIN, MAX, SUMX, AVERAGEX, COUNTX, MINX, and MAXX.
2. Date and time functions: DATE, YEAR, MONTH, DAY, HOUR, MINUTE, SECOND, NOW, and TODAY.
3. Text functions: CONCATENATE, UPPER, LOWER, PROPER, and LEN.
4. Logical functions: IF, SWITCH, and NOT.
5. Information functions: ISTEXT, ISNUMBER, ISBLANK, and ISTEXTBLANK.
6. Lookup functions: VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, and INDEX/MATCH combination.
7. Time intelligence functions: DATESYTD, TOTALYTD, SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR, and TOTALYTD.
8. Financial functions: IRR, NPV, XIRR, and XNPV.
9. Statistical functions: STDEV, VAR, and COVAR.
10. Date and time intelligence functions: TOTALYTD, SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR, TOTALYTD, and TOTALQTD.
11. Text manipulation functions: CONCATENATE, SUBSTITUTE, and REPLACE.
12. Filter functions: FILTER, CALCULATE, and ALL.
13. Time and date functions: NOW, TODAY, and DATE.
14. Table functions: SUMMARIZE, ADDCOLUMNS, and GROUPBY.
Beginners should be familiar with these frequently used functions comparable to those found in Excel.
- SUM — This function allows you to sum up a set of values from a column. For example, you can use the SUM function to find the total sales of your products. Syntax:
SUM(column_name)2. AVERAGE — This function allows you to calculate the average of a set of values from a column. For example, you can use the AVERAGE function to find the average price of your products. Syntax:
AVERAGE(column_name)3. COUNT — This function allows you to count the number of values in a column. For example, you can use the COUNT function to find the number of customers who purchased a product. Syntax:
COUNT(column_name)4. MIN — This function allows you to find the minimum value in a column. For example, you can use the MIN function to find the lowest price of your products. Syntax:
MIN(column_name)5. MAX — This function allows you to find the maximum value in a column. For example, you can use the MAX function to find the highest price of your products. Syntax:
MAX(column_name)6. IF — This function allows you to perform conditional statements in your calculations. For example, you can use the IF function to assign a value to a column based on a certain condition. Syntax:
IF(condition, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])7. VLOOKUP — This function allows you to look up values from a table based on a certain condition. For example, you can use the VLOOKUP function to find the sales of a product based on its product ID. Syntax:
VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])8. CONCATENATE — This function allows you to combine values from multiple columns into a single column. For example, you can use the CONCATENATE function to combine the first and last name of a customer into a single full name. Syntax:
CONCATENATE(column_name1, column_name2)9. TODAY — This function allows you to insert the current date into your calculation. For example, you can use the TODAY function to find the difference between the current date and a date in a column. Syntax:
TODAY()10. NOW — This function allows you to insert the current date and time into your calculation. For example, you can use the NOW function to find the time difference between the current time and a time in a column. Syntax:
NOW()In conclusion, DAX functions are a crucial tool for Power BI data processing. You may do intricate computations, transformations, and aggregations on your data with these functions, which will enable you to produce insightful insights, visuals, and reports. Understanding and using DAX functions is a crucial component of your Power BI skill set, whether you're a novice or an experienced user. These are only a handful of the DAX operations that Power BI supports. You can carry out a variety of data manipulations, computations, and transformations with these functions, which makes it simpler to evaluate and display your data in Power BI. Your Power BI skill set must include knowledge of and proficiency with DAX functions.
Don't forget to subscribe to
and join our Power BI community