⚡️ There are many HTML attributes — in addition to the basic ones, there are many incredibly useful and particularly potent attributes that can supercharge your website!
🚀 This article will unveil 24 powerful HTML attributes that can make your website more dynamic and interactive, ensuring a seamless and joyful experience for your users.
🔍 Let's dive in and explore these 24 powerful HTML attributes together!
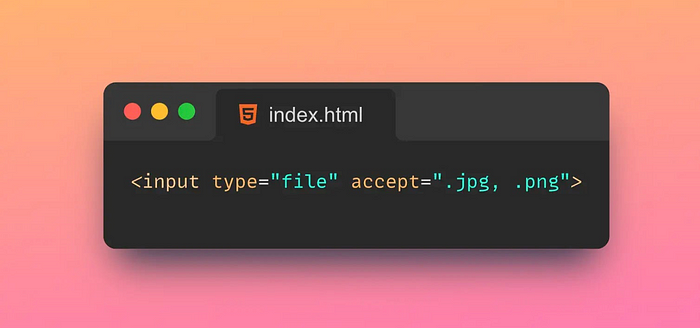
1.💾 Accept
The Accept attribute is used to specify a list of MIME types that the browser can handle.
Tips:
A MIME type is a standard for identifying the type of document,
For example, text/html represents an HTML document, image/jpeg represents a JPEG image, and so on.
💾 By including the Accept attribute in the HTTP request header, the browser can tell the server which MIME types it can 🤝 accept in response. Based on this information, the server can choose the most appropriate response type and return it to the browser. The value of the Accept attribute is a comma-separated list of MIME types, and wildcards can be used to represent a class of MIME types. For instance, text/* represents all text types.
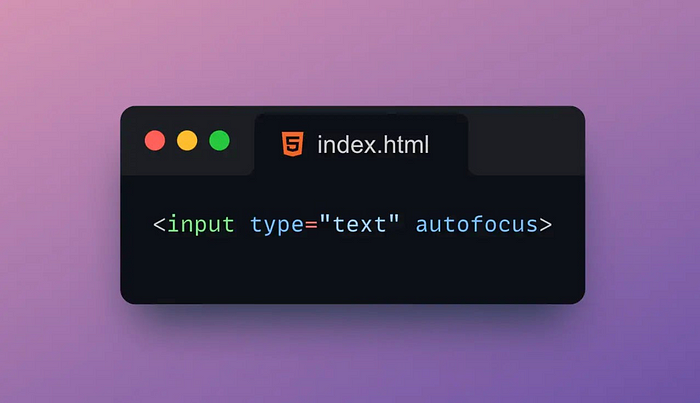
2. 🔍Autofocus
The Autofocus property is used to automatically set the focus to the specified element when the page loads.
Tips:
Autofocus attributes can be applied to various HTML elements such as text boxes, buttons, drop-down lists, and more.
In HTML5, the Autofocus attribute can omit the attribute value, indicating that the focus is set to the first element with the Autofocus attribute.
When the page is loaded, if there is an element with the Autofocus attribute, the browser will automatically focus the cursor on the element, so that the user can directly interact with the element without manually clicking or using the Tab key to switch focus.
3.📱 Input mode
The Inputmode attribute is an attribute for specifying the type of content entered in the text box.
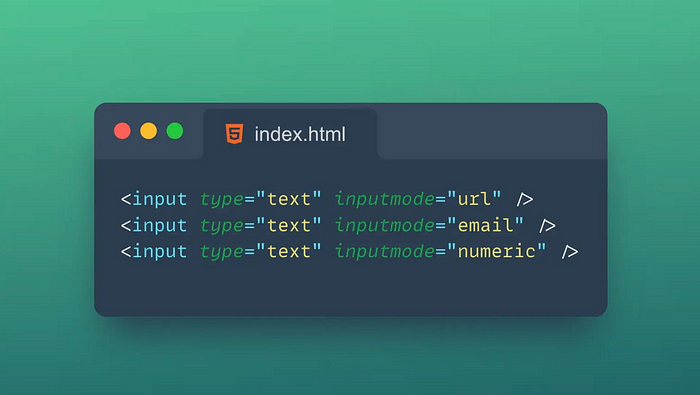
It can help the browser to better optimize the input experience, such as automatically popping up the appropriate virtual keyboard on mobile devices.
- ✏️
text: The default value, which means input any text. - 🚫
none: Indicates that no input is required. - 📞
tel: Indicates to enter a telephone number. - 🔗
url: Indicates the input URL address. - 📧
email: Indicates to enter an email address. - 🔢
numeric: Indicates the input number. - 🔟
decimal: Indicates inputting a number with a decimal point. - 🔍
search: Indicates to enter a search keyword.
The level of support for the Inputmode attribute may vary in different browsers.
Therefore, compatibility testing is required when using the Inputmode property.
4.🔢 Pattern
The Pattern attribute is a regular expression pattern used to specify the input content in the text box. It can help the browser to verify whether the content entered by the user conforms to the specified format requirements.
If the content entered by the user does not conform to the regular expression pattern specified by the Pattern attribute, the browser will display a default error message.
Tips:
- 📐
Pattern: The value of the Pattern attribute must be a valid regular expression. - 📝 Applicable only to text-based elements (e.g., text boxes, text fields, and password boxes).
- 🚫 The Pattern attribute will not prevent users from entering illegal characters but will verify that the input content meets the specified format requirements upon form submission.
- 💬 Customize the error message of the Pattern attribute using the
titleattribute.
The Pattern attribute is usually used together with the required attribute to ensure that the content entered by the user conforms to the specified format requirements and is not empty. For example, you can use the Pattern property to validate user input for zip codes, phone numbers, email addresses, and so on.
5. ✅Required
The Required attribute is an attribute used to specify whether a form element is required.
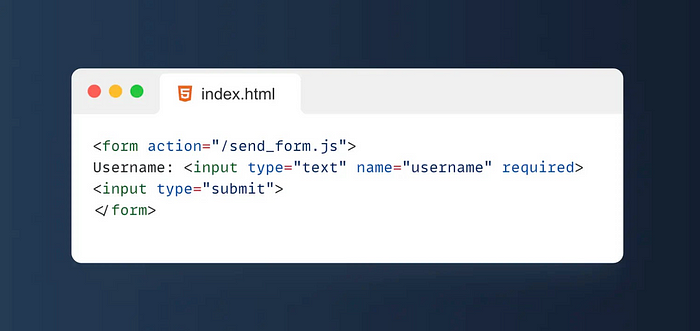
If a form element has the Required attribute set, then when the form is submitted, if the value of the element is empty, the browser will prevent the form from being submitted and prompt the user to fill in the field.
Tips:
- ✔️ Form-Specific: The
requiredattribute is strictly for input fields within a form; you cannot use it with non-input HTML elements. - 🚧 Functionality: Its sole purpose is to ensure that a particular field is not left empty before submitting the form. However, it doesn't inherently check whether the filled-in content meets any specific format.
- 🔳 Space and Whitespace: Interestingly, the
requiredattribute considers any input, including spaces, as valid content. To combat this, additional validation checks — either server-side or through other HTML attributes or JavaScript — are necessary to enforce non-whitespace or more complex content requirements. - 🔍 Pattern Matching: For format validation, the
requiredattribute can be paired with thepatternattribute. Thepatternattribute allows regex patterns to specify acceptable formats, ensuring user input adheres to a predefined structure (e.g., phone numbers, email addresses). - 👁️ Focus Management: The
autofocusattribute can indeed coexist with therequiredattribute on an input field. When used, it automatically places the cursor in the input field as soon as the form loads, streamlining the user experience especially for critical fields that need immediate attention.
The Required attribute is often used with the type attribute of form elements, such as text boxes, drop-down lists, radio boxes, check boxes, and so on.
6. 🖊️Autocomplete
The Autocomplete attribute is an attribute used to specify whether the form element has auto-complete enabled.
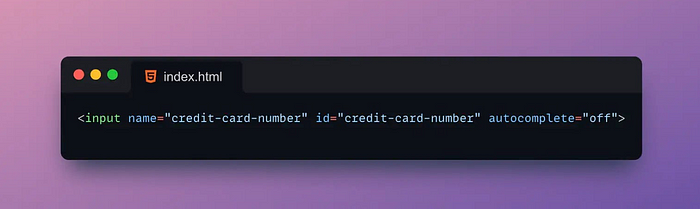
Autocomplete helps users fill out forms faster and reduces the chance of typing errors.
Tips:
- ✅
on: Activates the browser's autocomplete functionality, allowing it to fill in fields based on users' previous entries automatically. - ❌
off: Turns off autocomplete, preventing the browser from suggesting any previously entered values. - 👤
name: Signals the browser to suggest names based on previous entries in similar fields. - 📧
email: Directs the browser to suggest email addresses previously entered by the user. - 🔡
username: Indicates that the field should be filled with username suggestions from the browser's saved data. - 🔒
current-password: Tells the browser that the field expects a password, allowing it to suggest stored passwords for the current context. - 🔑
new-password: This is useful for account creation or password update forms where the browser should provide password suggestions or activate an integrated password generator. - 📞
tel: Prompts the browser to autocomplete telephone numbers based on previously entered information. - 🗺️
address-level1-address-level4: These levels advise the browser on which part of an address to suggest, from the broadest category (address-level1, typically a state or region within a country) down to more specific details like street names (address-level4). - 🌍
country: The browser is expected to suggest country names from its saved data.
The degree of support for the Autocomplete attribute may vary in different browsers. Therefore, compatibility testing is required when using the Autocomplete property.
7. 📊Multiple
The Multiple attribute is an attribute used to specify whether a form element allows multiple selections.
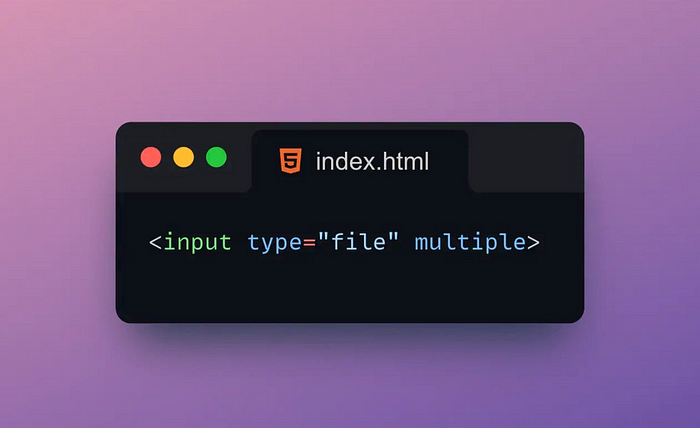
The Multiple attribute is typically applied to form elements such as dropdown lists, file uploads, and checkboxes.
Tips:
- ✔️ Specific Form Elements: The
multipleattribute is applicable to<select>and<input>elements of typefile. This attribute doesn't apply to checkboxes, as they inherently allow multiple selections by default, nor to text boxes and radio buttons, which are designed for single-entry inputs. - ✅ Boolean Attribute: The
multipleattribute is indeed a Boolean. When present, even without a value, it meanstrue. Conversely, when omitted, it defaults tofalse. - 🔳 Default Behavior: By default, the
multipleattribute is not applied, meaning the element only allows single selection (false).
🗃️ Enabling Multiple Selections:
- For a
<select>element: whenmultipleis set to true, users can select more than one option. - For an
<input type="file">: enablingmultipleallows users to select more than one file for upload.
If a form element has the Multiple attribute set, the user can select multiple options, not just a single one.
8. ⬇️Download
The Download attribute is an attribute for specifying a file name when a link downloads a file.
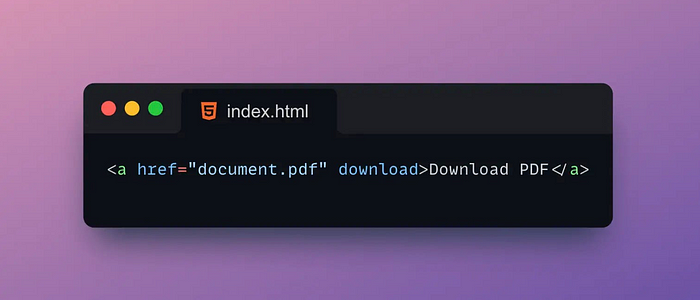
If a link is set with the Download attribute, then when the user clicks the link to download the file, the browser will save the file locally and use the file name specified by the Download attribute to name the file.
Tips:
- 📄 Any String: The value of the
downloadattribute can indeed be any string that specifies the default filename to be used for the downloaded file. This is the name that will be suggested to the user when they download the file. - 🔗
<a>Tag Specific: Thedownloadattribute is specifically designed for use with anchor (<a>) tags where you're providing a link to a resource like a file. - 🏷️ Naming Convenience: It's important to understand that while the
downloadattribute allows you to suggest a filename for the download, it does not alter the actual filename on the server; it only affects the name presented to the user. - 🖥️ Dynamic Filenames: Using JavaScript to dynamically assign or change the value of the
downloadattribute is possible and can be very useful for customizing the download experience. - 🛡️ Legal and Ethical Considerations: Ensuring that the use of the
downloadattribute for distributing files respects legal boundaries, copyright laws, and privacy rights is crucial. The content must be legitimately distributable to avoid legal repercussions and maintain ethical standards.
The Download attribute is usually used in tags to download PDF, image, audio, video and other files.
9. 🖋️Content editable
The Contenteditable attribute in HTML is an attribute used to specify whether an element is editable.
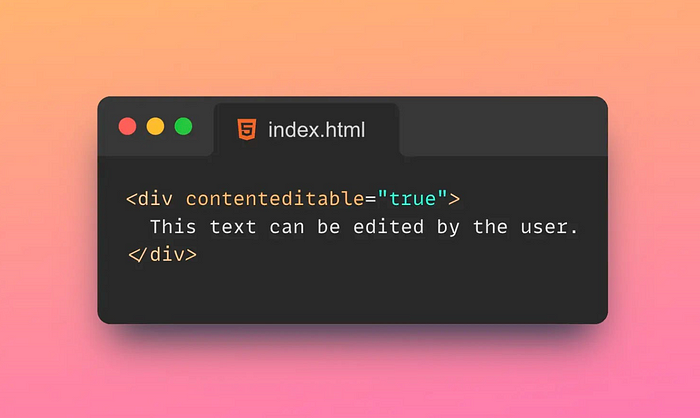
Tips:
- 🚫
false: By default, thecontenteditableattribute is set to "false." This implies the element is not editable, and the content is static — just like any regular HTML element's content. - ✏️
true: When thecontenteditableattribute is set to "true," it transforms the element into an editable area where users can modify the content. - 🔄
inherit: If thecontenteditableattribute is set to "inherit," the element's editability status is determined by its nearest ancestor with a definedcontenteditablestate.
⚠️ Additionally, it's crucial to be aware that:
- Setting an element as editable doesn't change its inherent behavior. For example, anchor (<a>) tags will still have their default navigation function unless otherwise scripted.
- Implementing
contenteditablerequires caution regarding web security. Enabling user-generated content can expose the site to XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) risks and malicious script injections. Always sanitize and validate user input on both the client and server sides to prevent security vulnerabilities.
If an element sets the Contenteditable attribute, then the user can enter text, insert pictures, modify styles, etc. in the element. The Contenteditable attribute is usually applied to, and other elements are used to implement functions such as rich text editors and editable tables.
10. 🚫Readonly
The Readonly attribute in HTML is an attribute used to specify whether a form element is read-only.
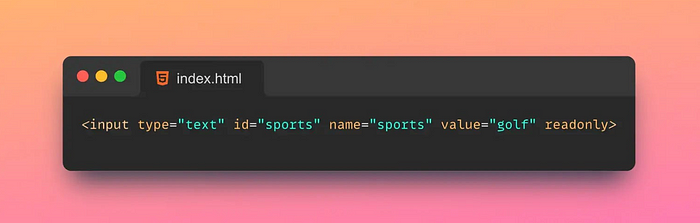
Tips:
- 🔓
false: The default state for thereadonlyattribute is "false," meaning that, unless specified, form elements are editable and the user can change the value. - 🔒
true: By setting thereadonlyattribute to "true," you make the form element non-editable, or read-only. Users can focus on and select the text within the element, but they cannot modify it.
⚠️ Things to consider:
- The
readonlyattribute does not prevent modifications via scripting; JavaScript can still alter the value of a read-only element. - Unlike the
readonlyattribute, thedisabledattribute not only prevents user modifications but also excludes the form element from being submitted with the form data. - When utilizing
readonlyattributes within a form, server-side handling is necessary to manage the associated values, as they are still submitted with the form. This might include storing these values in the backend with hidden fields.
If a form element has the Readonly attribute set, the user can see the value of the element, but cannot modify the value of the element. The Readonly attribute is usually applied to form elements such as text boxes, drop-down lists, and date pickers to display data or prevent users from modifying data.
11. 👀Hidden
The Hidden attribute is an attribute used to specify whether an element is hidden.
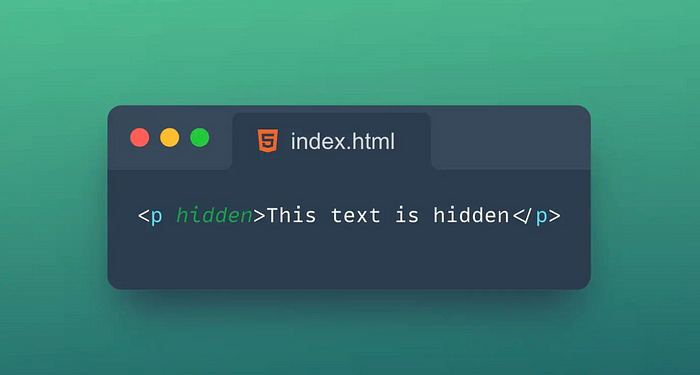
Tips:
- 👓
false: By default, thehiddenattribute's value is "false," which implies that the element is not hidden and will be displayed in the document as usual. - 🙈
true: When thehiddenattribute's value is set to "true," the element becomes hidden to the user. It is still present in the DOM (Document Object Model) but not visible on the page.
⚠️ It's important to note:
- The
hiddenattribute is not the same asdisplay: none;in CSS. The CSS propertydisplay: none;removes the element from the document flow as well as from the screen, whilehiddenjust makes the element invisible but still occupying its space in the layout. - Elements with the
hiddenattribute can still be interacted with using JavaScript or accessed by screen readers if not explicitly instructed otherwise. - When using the
hiddenattribute, especially in forms, you may need to manage its value in the backend script. For instance, if you're using a hidden field to store a value that should not be changed by the client.
If an element has the Hidden attribute set, the element will not be displayed on the page, but it still exists on the page and can be accessed through JavaScript, etc. The Hidden attribute is usually applied to elements such as form elements, buttons, images, etc., to pass data or control page behavior without affecting the page layout.
12. 📝Spellcheck
The Spellcheck attribute in HTML is an attribute used to specify whether to enable spell checking for an element.
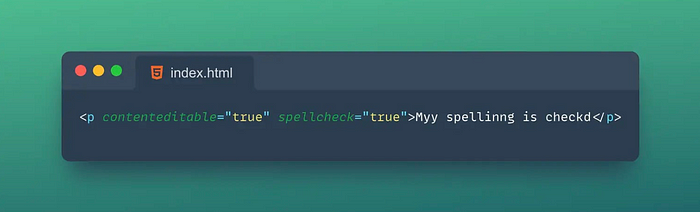
Tips:
✍️ true: When the value of the spellcheck attribute is "true," the element has spell checking enabled. This means the browser will underline misspelled words or grammatical errors, similar to what you'd experience in a word processing program.
❌ false: The default value of the spellcheck attribute is "false," indicating that the element does not have spell checking enabled by default.
⚠️ Additionally, remember:
- Support for the
spellcheckattribute can differ among web browsers. - Each browser may use its own spell check algorithms and dictionaries to identify potential errors.
- Security should always be a priority: when implementing the
spellcheckattribute, ensure that it does not lead to XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) attacks or allow malicious script injections.
If an element sets the Spellcheck attribute, then when the user enters text in the element, the browser will automatically check for spelling errors and display a red wavy line under the incorrect word. The Spellcheck attribute is usually applied to elements such as text boxes and text fields to improve the accuracy of user input.
13. 🈲Translate
The Translate attribute in HTML is an attribute used to specify whether an element should be translated.
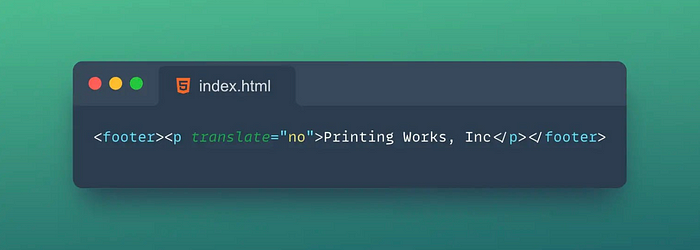
Tips:
- ✅
yes: The default value of thetranslateattribute is "yes," indicating that the element is expected to be translated when the page is processed by a translation tool. 🚫no: When the value of thetranslateattribute is "no," the element is marked as not to be translated.
⚠️ Keep in mind:
- The
translateattribute's support can vary across different web browsers. - Each browser may use different translation algorithms and dictionaries.
- Security is crucial: use the
translateattribute carefully to prevent XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) attacks and ensure that malicious scripts are not injected into your web pages.
If an element has the Translate attribute set, the browser will decide whether to translate the content of the element according to the value of the attribute. The Translate attribute is usually used in multilingual versions of websites to control which elements need to be translated and which elements do not.
14. ⏳Loading
The attribute in HTML loading is a new attribute that can be used to specify the browser's priority when loading resources.
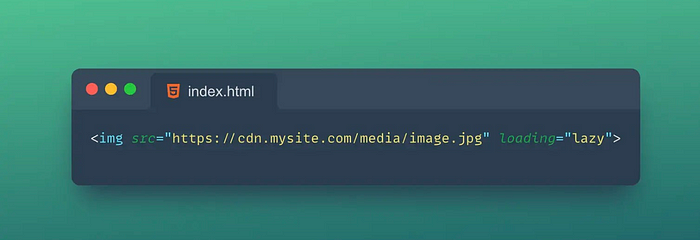
This attribute can be applied to tags such as <img>, <iframe>, <script>, <link> and <audio>.
Tips:
- 💤
lazy: Indicates that the resource should be lazily loaded after the page loads. It's the default value. - 🏃♂️
eager: Indicates that the resource should be loaded immediately on page load. - 🤖
auto: Indicates that the browser should decide when to load the resource by itself.
loading attributes are not supported by all browsers, so a compatibility check is required when using them.
15. ❌Onerror
onerror is a JavaScript event handler that fires on JavaScript errors.
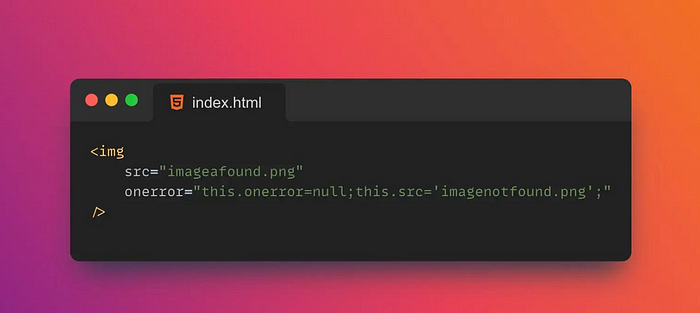
onerror event handlers can be added window to objects to catch JavaScript errors globally.
Tips:
- 🚫
message: "wrong information." (indicates the error message) - 🔗
source: The URL of the script where the error occurred. - 📈
lineno: The line number where the error occurred. - 📍
colno: The column number where the error occurred. - 🐞
error: An Error object containing detailed information about the error.
onerror event handlers can only catch JavaScript errors that are not caught by other error handlers.
It is best to use try-catch statements in your code to catch and handle JavaScript errors.
16. 📽️Poster
poster is an attribute of the HTML5 <video> tag that specifies an image to display before the video loads and before it plays.
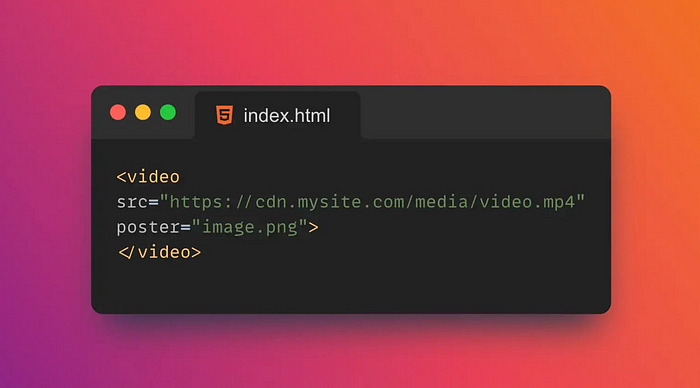
Tips:
poster attributes only apply to <video> tags, not <audio> labels.
It is commonly used to provide a preview image or thumbnail of a video.
17. 🎛️Controls
controls is an attribute of the neutral tag in HTML5 <video>, <audio> which is used to specify whether to display the controls of the media player.
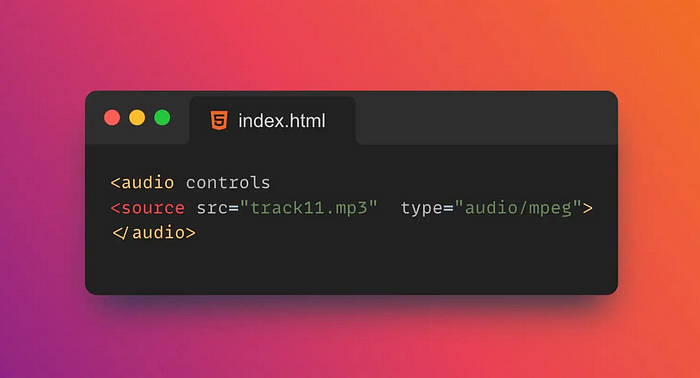
If controls the property is set to controls, controls are displayed on the media player, such as a play/pause button, volume control, progress bar, etc.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Controls Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<video width="320" height="240" controls>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="video.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
</body>
</html>`controls attributes are only available in browsers that support HTML5. If the browser does not support HTML5, the control will not be displayed.
18.▶️ Autoplay
autoplay is an attribute of the neutral tag in HTML5 <video> that <audio> specifies whether the media should play automatically on page load.
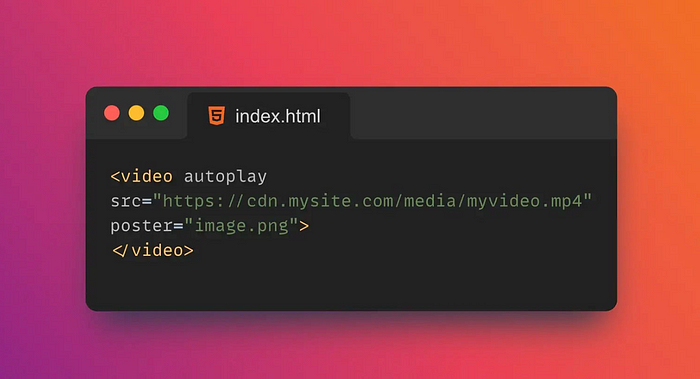
If autoplay the property is set to autoplay, the media will play automatically on page load.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Autoplay Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<video width="320" height="240" autoplay>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="video.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
</body>
</html>`Autoplay can negatively impact the user experience, so use autoplay attributes with caution. In some cases, browsers may block autoplay, such as on mobile devices, where the user must first interact with the page to allow autoplay.
19. 🔁Loop
loop is an attribute of the <video> neutral <audio> tag in HTML5 that specifies whether the media should loop after playback ends.
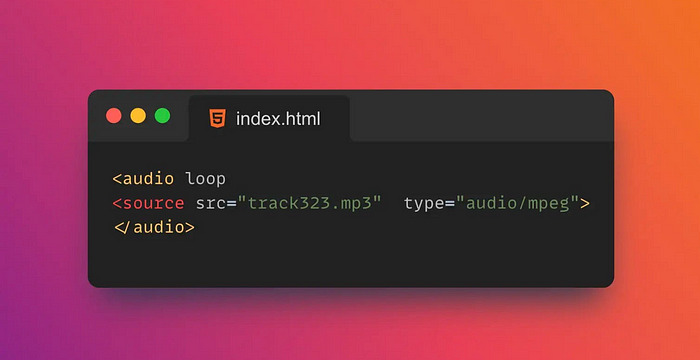
If loop the property is set to loop, the media will loop after playback finishes.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Loop Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<video width="320" height="240" loop>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="video.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
</body>
</html>`Looping can negatively impact the user experience, so use loop attributes with care.
20. 📑Cite
cite is a global attribute in HTML that can be used to specify the source of the citation.
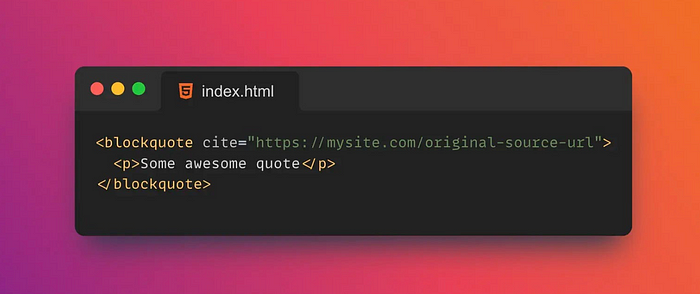
cite the value of the attribute should be a URL pointing to the source of the reference.
Tips:
cite attributes can be applied to tags such as <blockquote>, <q>, <del>, etc.<ins>
If the source of the referrer is not a URL, cite the value of the property can be set to a string describing the referrer.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Cite Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<blockquote cite="https://www.example.com/quote">
This is a quote from an external source.
</blockquote>
<q cite="https://www.example.com/quote">
This is a short quote from an external source.
</q>
<del cite="https://www.example.com/deleted">
This text has been deleted from an external source.
</del>
<ins cite="https://www.example.com/inserted">
This text has been inserted from an external source.
</ins>
</body>
</html>cite attributes do not automatically create links, so if you need to create a link, you need to use <a> a tag and href set the attribute as cite the value of the attribute.
21.📅 Datetime
datetime is an attribute of tags in HTML <time>, used to specify the date and time.
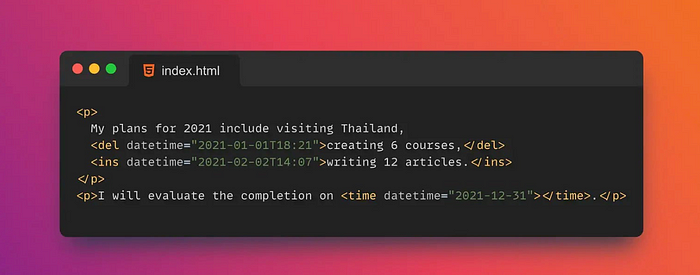
datetime the value of the attribute should be a valid date and time format, eg YYYY-MM-DDThh:mm:ss.
datetime attributes do not automatically format dates and times, so you need to use JavaScript or other tools to format dates and times.
22. ⚡Async
async is an attribute of the tag in HTML <script> that specifies whether the script should be loaded asynchronously.
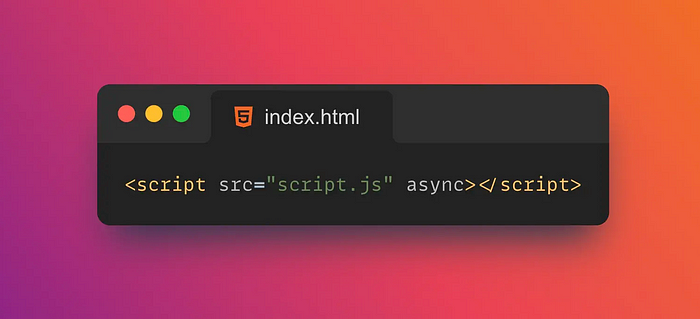
If async the property is set to async, the script will be loaded asynchronously and will not block parsing and rendering of the page.
Scripts loaded asynchronously may execute before the rest of the page loads, so use with caution. This can cause errors if the script depends on other parts of the page.
23. 🕒Defer
defer is an attribute of the tag in HTML <script> that specifies whether scripts should be lazy-loaded.
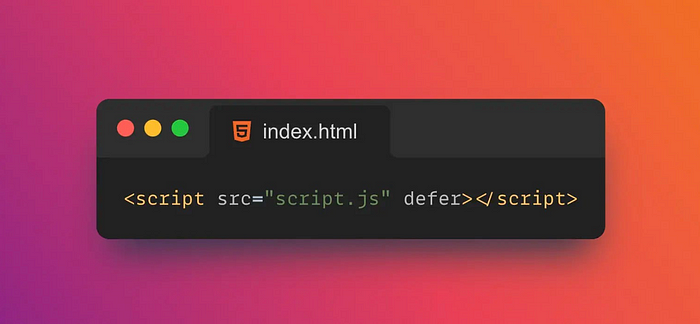
If defer the property is set to defer, the script will delay loading until the page has been parsed before executing it.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Defer Example</title>
<script defer src="script.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>In the example above, we defer set the property to defer, which will cause the script to be lazy loaded. In this case the script will be executed after the page has been parsed and will not block the page from loading.
24. 🖐️Draggable
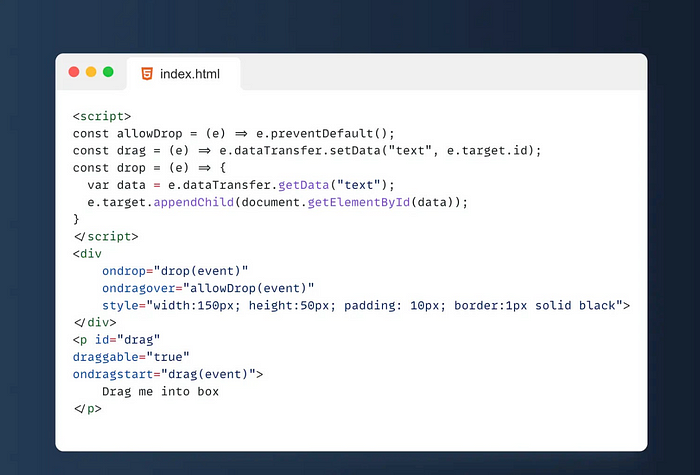
Draggable is an attribute in HTML5 that allows users to move elements by dragging them. draggable when an element is set to , the user can drag the element with the mouse or by touching the screen. When dragging an element, a series of events will be triggered, such as dragstart , drag and dragend, and these events can be used to implement the drag-and-drop function.
If you are a professional front-end engineer, you must have used many attributes!
Have you used all the 24 powerful attributes shared above in your project?