What is a Service Mesh?
A service mesh is a software layer used to manage, secure, and monitor inter-service communication in a microservices architecture. As communication between microservices becomes more complex, a service mesh steps in to direct traffic, increase fault tolerance (ensuring the service continues even if some components fail), and provide security and observability.
Objectives of Using a Service Mesh
- Traffic Management:
- Optimizes load distribution by balancing incoming traffic.
- Regulates service-to-service flow through traffic routing policies.
- Ensures retries of failed requests and timeout controls.
2. Security:
- Uses mutual TLS (mTLS) to encrypt inter-service communication.
- Provides authentication and authorization mechanisms.
3. Observability:
- Monitors service performance using metrics and logs.
- Supports fault detection and analysis processes.
4. Fault Tolerance and Resilience:
- Circuit breakers: Stop incoming requests when a defined failure threshold is reached, preventing system overload and allowing automatic recovery.
- Traffic shaping: Optimizes network traffic by prioritizing and delaying incoming requests to ensure efficient resource use and continuous operation of critical services.
Use Cases of Service Mesh
- Managing service-to-service communication in distributed systems.
- Ensuring security and observability in microservices-based applications.
- Improving performance in applications with high traffic demands.
- Providing solutions for infrastructures with security and monitoring requirements.
Advantages
- Easy Security Integration: Provides data encryption and authentication.
- Dynamic Traffic Management: Enhances efficiency with load balancing and fault management.
- Service Independence: Ensures services operate independently.
- Visibility and Observability: Offers detailed analysis and reporting capabilities.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Requires additional management and configuration.
- Performance Impact: May increase resource consumption.
- Learning Curve: Adapting to new technologies can take time.
What is Istio?
Istio is a service mesh solution designed for applications using a microservices architecture. It helps manage, secure, and observe inter-service communication. Istio integrates with Kubernetes to provide traffic management, security, and observability.
Key Features of Istio
- Traffic Management:
- Load Balancing: Directs traffic to different service instances using random, round-robin, or weighted algorithms.
- Traffic Routing: Routes incoming traffic based on defined rules, supporting deployment strategies such as Canary and Blue/Green.
- Canary Deployment: Gradually routes traffic to a new version for testing.
- Blue/Green Deployment: Deploys a new version in a separate environment while the existing version remains live.
- Retry and Timeout Policies: Improves application resilience by retrying failed requests and setting timeouts to prevent resource wastage.
2. Security:
- mTLS (Mutual TLS Encryption): Encrypts all service-to-service traffic for enhanced security.
- Authentication: Supports standards like JWT (JSON Web Token) and OAuth.
- Authorization Policies: Fine-grained access control mechanisms for service access.
3. Observability:
- Metrics: Collects detailed performance metrics with tools like Prometheus.
- Logging: Provides comprehensive logs for traffic and error tracking.
- Tracing: Integrates with tools like OpenTelemetry and Jaeger for distributed tracing.
4. Policy Management:
- Access Control Policies: Regulates which users and services can access specific resources.
- Quota and Rate Limiting: Prevents service overload by limiting request rates.
Use Cases of Istio
- Microservices-based applications.
- Large-scale distributed systems.
- Applications requiring high traffic management and security.
- Industries such as finance, e-commerce, and telecommunications.
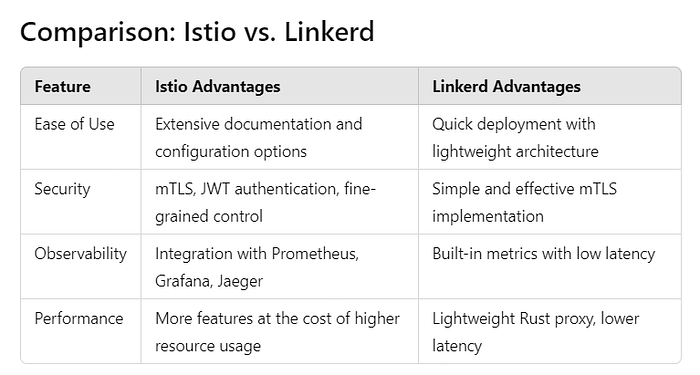
Advantages
- Secure communication between services.
- Flexible control with traffic routing and policies.
- Easier service observability and error analysis.
- Deep integration with Kubernetes.
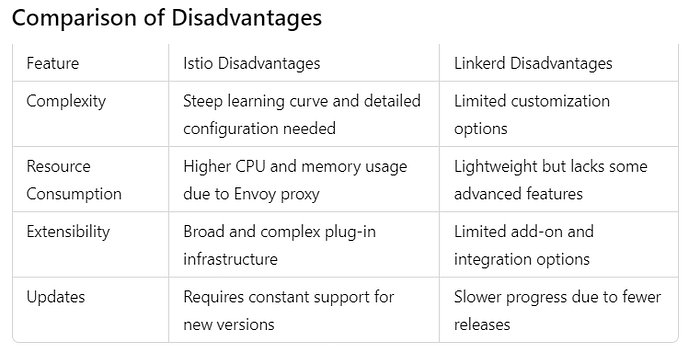
Disadvantages
- Complex setup and management.
- Additional resource consumption.
- Steep learning curve.
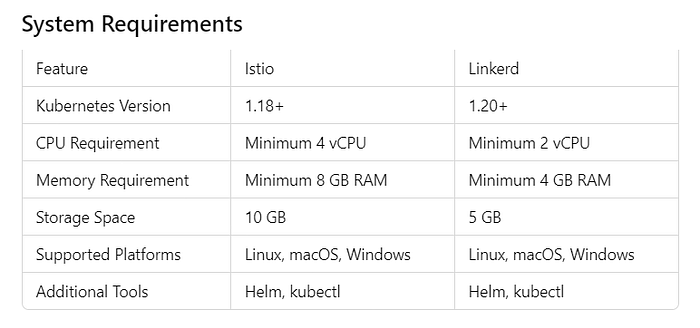
System Requirements:
- Kubernetes cluster (1.18+)
- 4 vCPU and 8 GB RAM (minimum)
- Helm and kubectl installed
What is Linkerd?
Linkerd is a lightweight and simple service mesh solution designed for microservices-based applications. It manages inter-service communication securely and efficiently while focusing on performance, simplicity, and reliability. It integrates with Kubernetes and offers an easy-to-use solution.
Key Features of Linkerd
- Traffic Management:
- Load Balancing: Optimizes load distribution across service instances.
- Traffic Redirection: Ensures the optimal path for service requests.
- Timeouts: Terminates unresponsive services to maintain system performance.
- Retry Mechanisms: Automatically retries failed requests based on defined policies.
2. Security:
- Mutual TLS (mTLS) Encryption: Encrypts all inter-service traffic for privacy and security.
- Authentication: Provides reliable authentication mechanisms.
- Authorization Policies: Implements fine-grained access control for inter-service communication.
3. Observability:
- Real-time Metric Collection: Provides operational visibility.
- Prometheus Integration: Enables real-time metric analysis.
- Grafana Visualization: Offers user-friendly graphical analysis.
- Jaeger Tracing: Tracks service interactions for troubleshooting.
4. Automatic Proxy Injection:
- Kubernetes Integration: Automatically injects Linkerd proxy components into pods.
- Transparent Service Management: Secures traffic without code changes.
Advantages
- Easy to install and use.
- Optimized for performance with low memory and CPU consumption.
- Secure inter-service communication.
Disadvantages
- Limited feature set compared to Istio.
- May not be suitable for highly customized projects.
Use Cases of Linkerd
- Microservices-based applications.
- Infrastructure requiring security and monitoring.
- Lightweight service mesh needs.
System Requirements:
- Kubernetes cluster (1.20+)
- 2 vCPU and 4 GB RAM (minimum)
- Helm and kubectl installed
When to Choose Which?
Choose Istio if:
- A large corporate system requires a broad feature set.
- High traffic management and detailed observability are needed.
- Enterprise support and long-term large integrations are required.
Choose Linkerd if:
- A project requires quick and easy setup.
- A performance-focused and lightweight solution is needed.
- Minimal resource consumption is desired for small to medium-sized projects.
Conclusion
The choice between Istio and Linkerd depends on project requirements and resource capacity. Istio offers a more complex and comprehensive service mesh solution, whereas Linkerd excels in performance and simplicity.