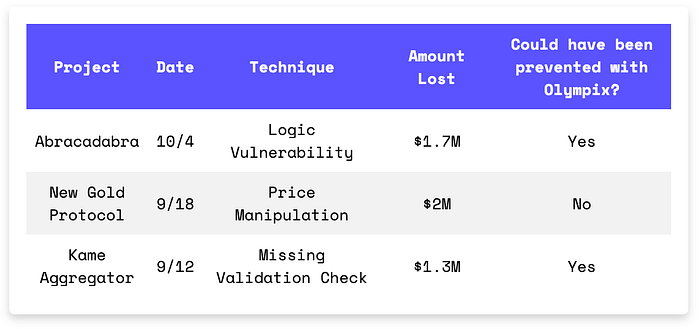
Three exploits, one theme: broken contract boundaries. Abracadabra's cook() logic disabled its own collateral checks. New Gold Protocol let flash loans distort its AMM price. Kame Aggregator opened the door to malicious multicalls. If your protocol blindly trusts inputs, defaults, or delegatecalls — you're not secure.
In Brief
- Abracadabra lost $1.7M because the cook() function cleared solvency checks and allowed the attacker to borrow without collateral.
- New Gold Protocol lost $2M due to a price manipulation attack using flash loans.
- Kame Aggregator lost $1.3M when swap() allowed arbitrary external calls.
Hacks Analysis
Abracadabra | Amount Lost: $1.7M
On October 4th, the Abracadabra exploit on the Ethereum Mainnet resulted in a $1.7M loss. The root cause of the exploit was a logic vulnerability in the CauldronV4 contract's cook() function. The attacker called this function with actions [5, 0]. Action 5 (ACTION_BORROW) borrowed funds and set status.needsSolvencyCheck = true. Action 0 was undefined, so the 'else' in the if statement executed _additionalCookAction(), which cleared needsSolvencyCheck and skipped collateral verification. The attacker then borrowed assets without collateral and made a profit.
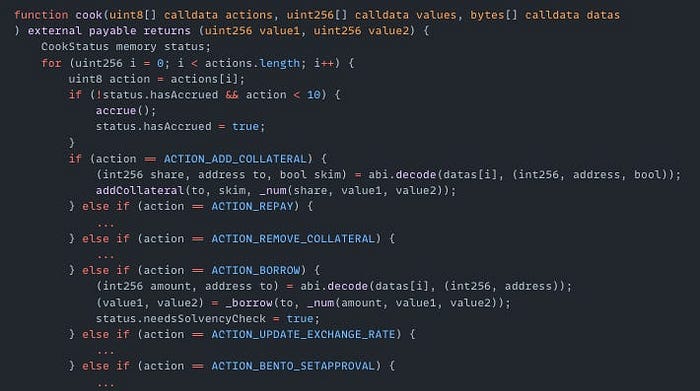
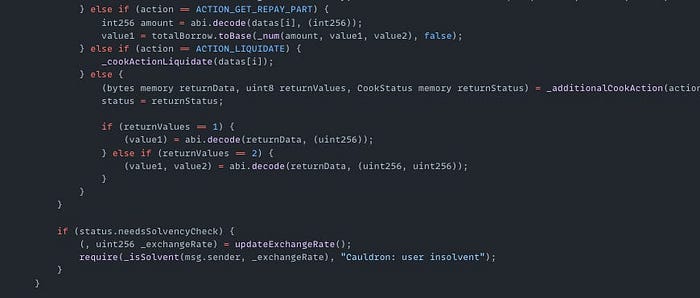
Exploited Contract: 0x5e70f7acb8ec0231c00220d11c74dc2b23187103
Transaction: 0x842aae91c89a9e5043e64af34f53dc66daf0f033ad8afbf35ef0c93f99a9e5e6
New Gold Protocol | Amount Lost: $2M
On September 17th, the New Gold Protocol exploit on the BNB Chain resulted in a $2M loss due to a price manipulation attack. The attacker first borrowed $211M using flash loans and used it to reduce the NGP balance on PancakeSwap from 477K to 0.035. This reduced NGP liquidity, artificially inflated the token price and allowed the attacker to make a profit.
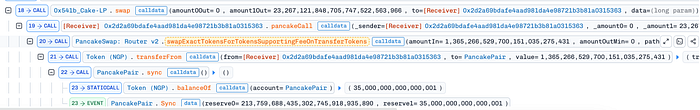
NGP Token Contract (on BSC): 0xd2f26200cd524db097cf4ab7cc2e5c38ab6ae5c9
Transaction: 0xc2066e0dff1a8a042057387d7356ad7ced76ab90904baa1e0b5ecbc2434df8e1
Kame Aggregator | Amount Lost: $1M
On September 12th, the Kame Aggregator exploit on Sei resulted in a $1.3M loss. The root cause of the exploit was that the swap() function allowed arbitrary external calls without validation. The attacker exploited this by passing a malicious Multicall contract as the executor parameter. This allowed the attacker to drain funds from 830 users who had granted token approvals to the router. The attack succeeded because users had set unlimited or excessive allowances for the AggregationRouter contract.
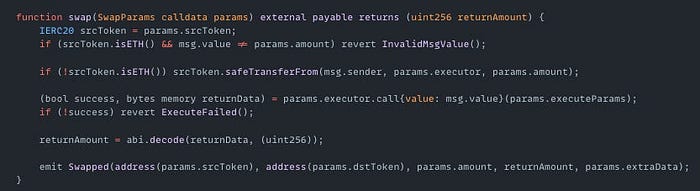
Exploited Contract (on SEI): 0x14bb98581ac1f1a43fd148db7d7d793308dc4d80
Transaction: 0x1bf7a70c0f55344d3466fbce42317fbc842c29a25d1ed86253a2cc64163dfdc2
Olympix: Your Partner in Secure Smart Contracts
Olympix provides advanced Solidity analysis tools to help developers identify and fix vulnerabilities before they become critical exploits.
Get started today to fortify your smart contracts and proactively shield them from exploits in the evolving Web3 security landscape.
Connect with us on:
Twitter | LinkedIn | Discord | Medium | Instagram | Telegram | Newsletter
