"Search Engines" such as Google are huge indexers — specifically, indexers of content spread across the World Wide Web.
These essentials in surfing the internet use "Crawlers" or "Spiders" to search for this content across the World Wide Web.
Task 2 : Let's Learn About Crawlers
Crawlers (also called web spiders or bots) are automated programs used by search engines (like Google) to discover and collect information from websites.
— Discovery Methods:
- Pure Discovery: Crawlers visit a URL directly and gather information about its content type.
2. Following Links: They find and follow all URLs (links) found on previously crawled websites, expanding their reach across the web. This is like a "virus" spreading to everything it can.
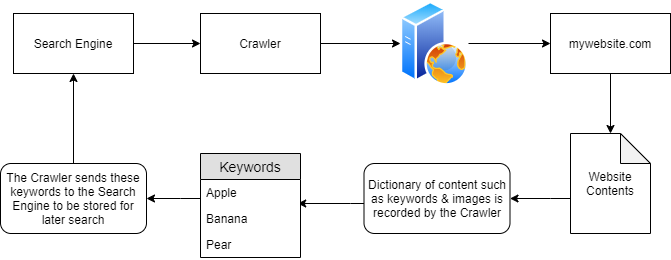
How crawlers Build a Search Engine's Knowledge???
- Initial discovery (domain)
- Indexing Content (it reads and processes the entire content of the domain)
- Keyword Extraction (keywords / relevant data)
- Storing Information (These keywords are stored in dictionary associated w/ the domain)
- Reporting/ sending the information back to search Engine
- Persistence

CRAWLERS are Traversal
Traversal (Spreading out) — crawlers visit every URL and find they can find. It also follows linked websites and it would proceed to crawl it.
Q&A:
Name the key term of what a "Crawler" is used to do. This is known as a collection of resources and their locations
Correct Answer: Indexing (or Web Indexing)
What is the name of the technique that "Search Engines" use to retrieve this information about websites?
Correct Answer: Crawling (or Web Crawling)
What is an example of the type of contents that could be gathered from a website?
Correct Answer: Keywords (or text content, links, images, etc.)
Task 3 : Enter: Search Engine Optimisation
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of improving a website's visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) to attract more "organic" (unpaid) traffic. It's a highly important and profitable field.
Search engines use complex algorithms to rank domains, considering many factors. Some Factors :
- Responsiveness
- Crawlability
- Keywords
- Algorithms
- Paid Advertising
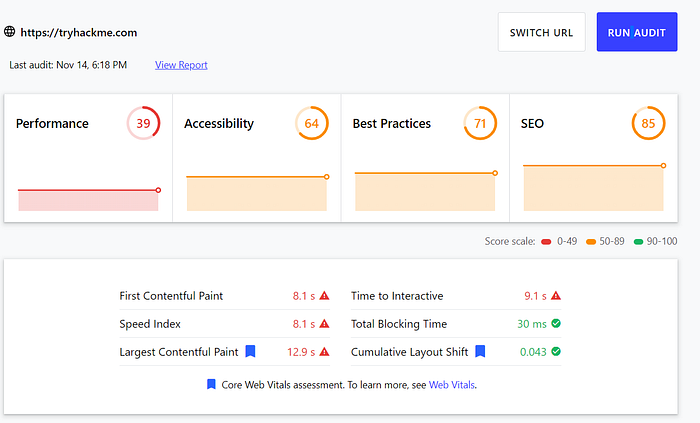
Use the same SEO checkup tool and other online alternatives to see how their results compare for https://tryhackme.com and http://googledorking.cmnatic.co.uk
Task 4 : Robots.txt
robots.txt is a text file that tells web crawlers (like Googlebot, Bingbot) which parts of a website they can or cannot access and index. It acts as a set of guidelines for crawlers.
It must be located at the root directory of a website (e.g., http://example.com/robots.txt).
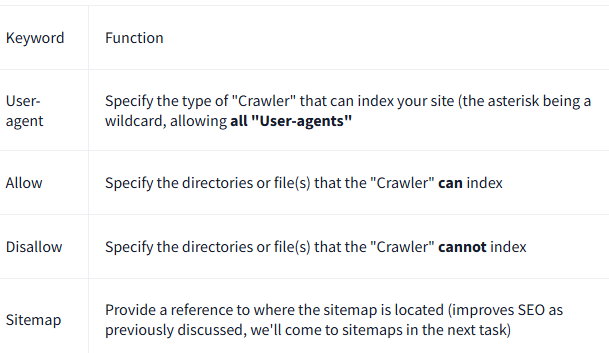
Basic robots.txt Examples:
> Allow all crawlers to index everything:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Sitemap: http://mywebsite.com/sitemap.xml> Hide specific directories/files:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /super-secret-directory/
Disallow: /not-a-secret/but-this-is/
Sitemap: http://mywebsite.com/sitemap.xmlCrawlers will avoid
/super-secret-directory/and the sub-directory/not-a-secret/but-this-is/(but will index other content within/not-a-secret/).
> Allow only specific crawlers:
User-agent: Googlebot
Allow: /
User-agent: msnbot
Disallow: /Only
Googlebotcan index the site;msnbotis blocked from the entire site.
Q&A:
Where would "robots.txt" be located on the domain "ablog.com"?
Correct Answer:
http://ablog.com/robots.txt
If a website was to have a sitemap, where would that be located?
Correct Answer: It's usually located at the root, for example,
http://ablog.com/sitemap.xml. The exact location would be specified in therobots.txtfile itself.
How would we only allow "Bingbot" to index the website?
Correct Answer:
User-agent: Bingbot
Allow: /
User-agent: *
Disallow: /How would we prevent a "Crawler" from indexing the directory "/dont-index-me/"?
User-agent: *
Disallow: /dont-index-me/What is the extension of a Unix/Linux system configuration file that we might want to hide from "Crawlers"?
Correct Answer:
.conf(e.g.,apache.conf,nginx.conf) or.cfg. These files often contain server configurations, paths, or even credentials.
Task 5 : Sitemaps
- Sitemaps are like geographical maps for websites. They provide a structured list of all the important pages and content on a website, indicating the "routes" for crawlers to find information.
They help search engine crawlers efficiently discover and index content on a domain.
File Format: Sitemaps are usually in XML (Extensible Markup Language) format.
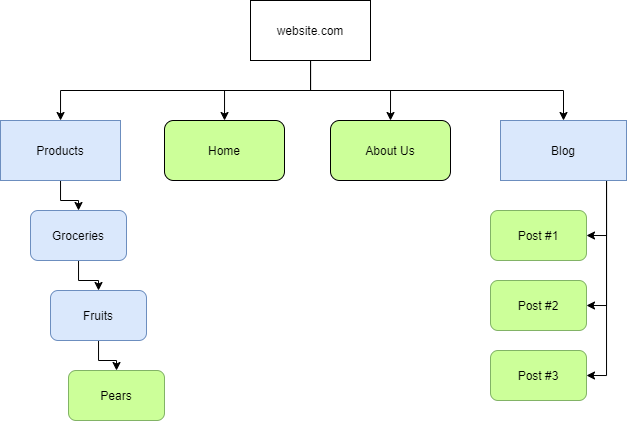
Why are Sitemaps Important for SEO?
- Improved Crawling Efficiency
- "lazy" Search engines
- SEO Optimization
- The easier a website is to crawl,the more optimised it is for the Search Engine
Structure Analogy:
- Blue Rectangles (Illustrative): Represent "routes" or directories (e.g., "Products," "Blog").
- Green Rounded-Rectangles (Illustrative): Represent actual individual pages or content (e.g., specific product pages, blog posts).
Q&A
What is the typical file structure of a "Sitemap"?
Correct Answer: XML (Extensible Markup Language)
What real life example can "Sitemaps" be compared to?
Correct Answer: Geographical maps (or street maps, road maps)
Name the keyword for the path taken for content on a website
Correct Answer: Route
Task 6 : What is Google Dorking?
Google Dorking is a technique that utilizes advanced search operators to uncover information on the internet that may not be readily available through standard search queries.
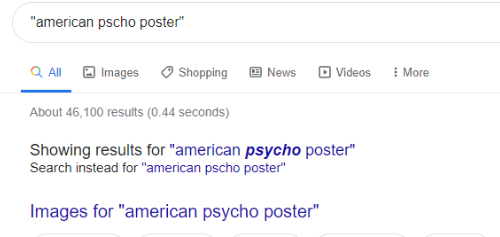
Quotation Marks (""):
> This will be specific/exact phrase and filter out the irrelevant results
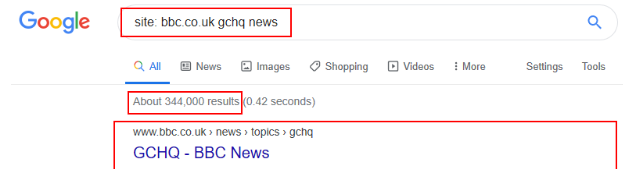
site: Operator:
SYNTAX:
site:example.com [your query]> Restricts your search to a specific domain or website.
>This is Excellent for finding information on a particular website that might be buried or hard to navigate directly.
filetype: Operator:
SYNTAX:
filetype:ext [your query]> Searches for files with a specific extension.
cache: Operator:
Format:
cache:url> Can show what a page looked like at a previous point in time, even if the live page has been changed or removed.
intitle: Operator:
SYNTAX:
intitle:"your phrase"> Requires the specified phrase to appear in the title of the web page.
TAKE NOTE!
By using special "operators" (similar to programming language operators), you can refine searches, perform specific actions, and filter results.
Q&A:
What would be the format used to query the site bbc.co.uk about flood defences?
site:bbc.co.uk "flood defences"
What term would you use to search by file type?
filetype:
What term can we use to look for login pages?
intitle:login

