أَوَلَمْ يَعْلَمُوا أَنَّ اللَّهَ يَبْسُطُ الرِّزْقَ لِمَن يَشَاءُ وَيَقْدِرُ ۚ إِنَّ فِي ذَٰلِكَ لَآيَاتٍ لِّقَوْمٍ يُؤْمِنُونَ [ الزمر: 52] الحمد لله رب العالمين، الذي جعل لكل شيء قدرًا، وجعل لكل قدرِ أجلًا، وجعل لكل أجلِ كتابًا، الحمد لله رب العالمين، حمدًا لشُكرهِ أداءً ولحقّهِ قضاءً، ولِحُبهِ رجاءً، ولفضلهِ نماءً، ولثوابهِ عطاءً، الحمد لله رب العالمين، الذي سبحت له الشمس والنجوم الشهاب، وناجاه الشجر والوحش والدواب، والطير في أوكارها كلُ له أواب، فسبحانك يا من إليه المرجع والمآب
Let me walk you through how I found a Business Logic flaw in one of the most famous online stores worldwide. The issue was specifically a Price Manipulation vulnerability. For confidentiality reasons, I'll refer to it as target.com, since the bug is still unresolved. By the way, the program was external.
Recon & Targeting
The first step was to choose a target to test 😈 My focus was on finding a bug in the application logic. Once I set my scope to target.com, I decided to purchase a product priced at $96.

I proceeded to the checkout flow at target.com/checkout, selected PayPal as the payment option, and turned on Burp Suite Intercept.
Here's where things got interesting: I modified the Price parameter in the request to my desired value — in this case, $60.

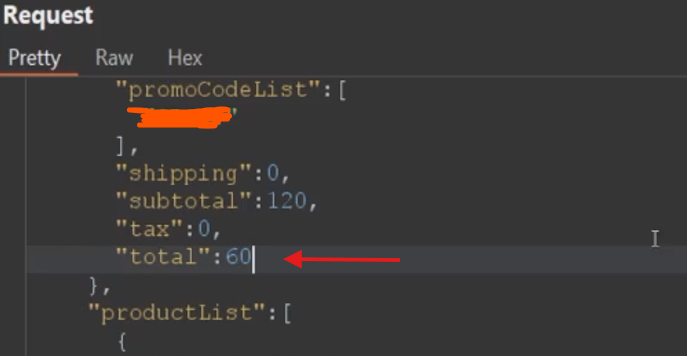
I forwarded the request and BOOM 🚀 the price was updated successfully, and I was redirected to the PayPal payment gateway with the manipulated amount 🔥
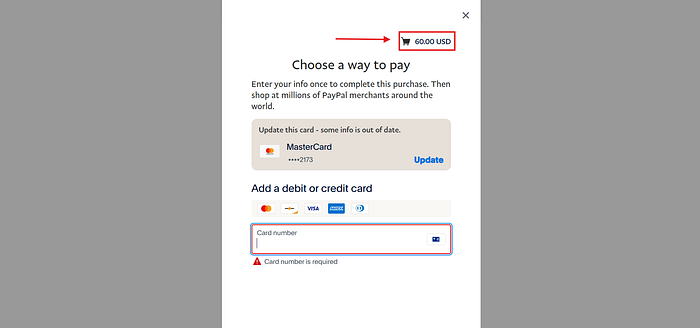

Why Does This Happen?
This occurred because of over-trusting client-side input, especially with sensitive fields like product prices. The application failed to validate the request server-side.
To prevent such issues, the server must enforce strict checks on critical values such as product price, quantity, and IDs — never relying solely on client-side data.
The Bounty?
The big question: "How much bounty did you receive?" Unfortunately… the bug was already reported before me, and my submission was closed as a Duplicate 😢

If you enjoyed this write-up or want to connect, you can find me on Instagram : zyad_ibrahim333
