In the fast-paced world of software development, speed and agility are everything. Developers are under constant pressure to ship features faster, adopt the latest frameworks, and keep up with user expectations. Open-source software (OSS) has become the cornerstone of this acceleration — today, over 90% of modern applications contain open-source components.

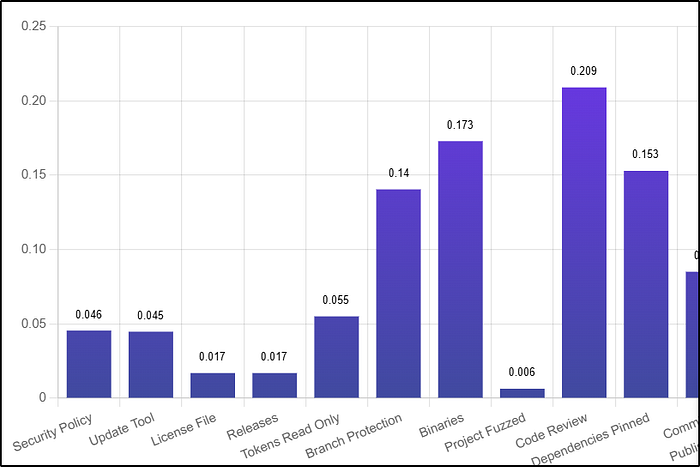



But with speed comes risk. Every piece of open-source code your application depends on introduces potential vulnerabilities, licensing issues, and hidden risks into your software supply chain. And here's the catch: attackers know it. From Log4Shell to the SolarWinds incident, software supply chain attacks have become one of the biggest threats to organizations worldwide.
This is where Software Composition Analysis (SCA) comes in.
In this blog, we'll break down what SCA is, why it's critical, how it works, and the best practices to integrate it seamlessly into your development lifecycle. Whether you're a developer, DevOps engineer, or security professional, by the end of this article, you'll understand how to leverage SCA to safeguard your applications without slowing down innovation.
What is Software Composition Analysis (SCA)?
Software Composition Analysis (SCA) is a security practice and set of tools that help organizations identify, manage, and mitigate risks in the open-source and third-party components used within their software applications.
At its core, SCA answers three key questions:
- What's in my code? Identify all open-source libraries, frameworks, and third-party dependencies.
- Is it safe? Detect known vulnerabilities (CVEs) and security risks in those components.
- Is it compliant? Check for licensing obligations and ensure you're not violating open-source licenses.
Think of SCA as an X-ray for your software supply chain. While static analysis (SAST) scans your custom code and dynamic analysis (DAST) tests running applications, SCA dives into your dependencies and their transitive dependencies (libraries used by other libraries) to reveal hidden risks.
Why Does SCA Matter?
The importance of SCA stems from three interconnected realities of modern software development:
1. The Open-Source Dependency Explosion
Developers no longer build everything from scratch. Instead, they rely on ecosystems like npm, Maven, PyPI, and NuGet. While this accelerates development, it also creates a sprawling dependency graph.
A single npm package might depend on dozens of other packages, each with its own risks. Without visibility, it's almost impossible to know what's inside your application.
2. Rising Software Supply Chain Attacks
According to Gartner, by 2025, 45% of organizations will experience a software supply chain attack, up from 15% in 2021. High-profile incidents like:
- Log4Shell (2021): A critical zero-day in Log4j, a widely used Java logging library, exposed thousands of organizations.
- SolarWinds (2020): Attackers inserted malicious code into a software update, impacting U.S. government agencies and Fortune 500 companies.
These incidents highlight that attackers don't need to breach your code directly — exploiting third-party components is often easier and more scalable.
3. Compliance and Licensing Risks
Beyond security, open-source software comes with licenses (such as MIT, GPL, Apache 2.0, etc.) that dictate how the software can be used, modified, or distributed. Ignoring these can lead to legal disputes, fines, or forced code rewrites.
SCA tools ensure you're compliant with these obligations, protecting both your business and your intellectual property.


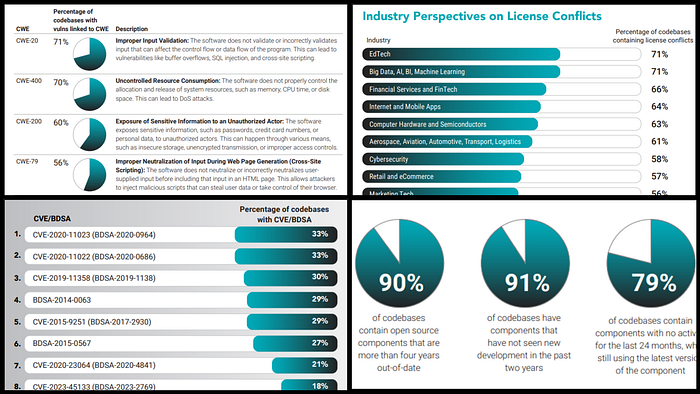
⚠ Read full report here: https://www.blackduck.com/content/dam/black-duck/en-us/reports/rep-ossra.pdf
1. Ubiquity and Rapid Growth of Open-Source
Open-source software is not just common — it's foundational. A 2024 Synopsys study found that 96% of commercial codebases contain open-source components, and 77% of the code within them is open-source. Complementing that, a 2022 Linux Foundation study estimated that 70–90% of any given codebase is OSS.
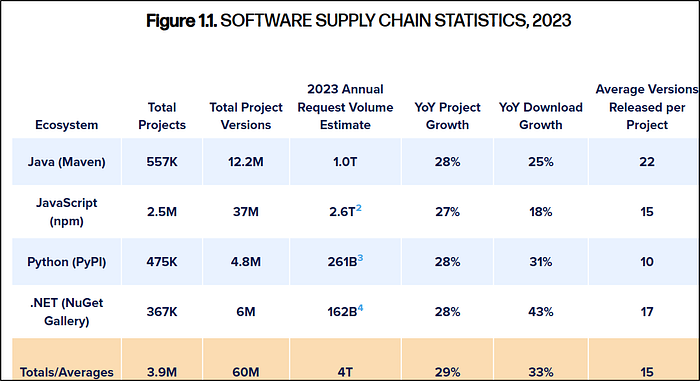
The scale of the ecosystem is staggering. The number of project releases on npm surged from 1 million in June 2019 to 3.6 million in 2022. Sonatype's 2023 report shows combined annual releases across Maven, npm, PyPI, and NuGet totaled 60 million versions, with a 29% year-over-year growth in new projects.
Link: https://www.sonatype.com/state-of-the-software-supply-chain/2023/open-source-supply-and-demand
2. Escalating Vulnerabilities and Risk Exposure
The vulnerability landscape is worsening dramatically:
- Synopsys' 2024 OSSRA report revealed that 74% of codebases contain high-risk open-source vulnerabilities — up from 48% the previous year, a 54% increase.
- Related findings: 91% of codebases include components that are 10+ versions outdated, and nearly half (49%) use completely inactive components; average vulnerability age exceeds 2.5 years, with 25% of components having vulnerabilities older than 10 years.
From a broader perspective, Synopsys 2020 data highlighted that:
- The average application depends on more than 500 OSS components (a 77% jump from 298 just two years prior).
- 84% of applications contained at least one vulnerability (up from 60%), with the typical app having 158 vulnerabilities and 60% harboring at least one high-severity issue.
3. Layered Risks: Beyond CVEs
Security threats extend far beyond known vulnerabilities:
- OWASP's Top 10 OSS Risks include operational hazards such as unmaintained software, typo-squatting/name confusion attacks, license risks, and untracked dependencies — many of which do not result in CVEs but pose serious threats nonetheless.
- Their report noted that 89% of codebases contain OSS older than 4 years, and 91% include components with no development activity for over two years.
- Additionally, 95% of vulnerabilities lurk in transitive dependencies, many of which are invisible without proper tooling.
Link: https://owasp.org/www-project-open-source-software-top-10/
4. Economic Stakes and Hidden Costs
The financial and operational impact of relying on OSS is significant:
- SentinelOne estimates open-source saves firms $8.8 trillion, indicating that without OSS, organizations would need to spend 3.5 times more to build equivalent functionality.
- But this massive value is undermined by the chaotic and sometimes unmonitored nature of OSS-where contributions come from varied sources, and not all maintainers adhere to robust security practices.
Link: https://www.sentinelone.com/cybersecurity-101/cybersecurity/open-source-software-security-risks/
5. Supply Chain Threats and License Liabilities
Supply chain risks are climbing:
- Famous incidents like Log4Shell and SolarWinds underscore how attackers exploit trusted components to propagate damage. SCA is vital to detect and respond to such threats early.
- Beyond security, licensing is a hidden minefield: Synopsys found 53% of codebases contained license conflicts, and 31% used code with no clear license — creating legal and compliance risks.
How Does SCA Work?
SCA tools typically follow a structured process to uncover and manage risks:
1. Inventory Creation (Bill of Materials) The tool scans your codebase, container images, or CI/CD pipeline to build a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) — a comprehensive list of all components and dependencies.
2. Vulnerability Detection The SBOM is matched against vulnerability databases like:
- NVD (National Vulnerability Database)
- GitHub Security Advisories
- OSS Index, Snyk DB, etc. This helps identify known CVEs in your dependencies.
3. License Compliance Check Each component is checked for license type and restrictions, ensuring you're not inadvertently violating legal terms.
4. Risk Prioritization Not all vulnerabilities are equally dangerous. SCA tools often factor in:
- CVSS severity scores
- Exploit availability
- Component usage context (e.g., is the vulnerable function even invoked?)
5. Remediation Guidance The tool recommends fixes, such as upgrading to a patched version, replacing the component, or applying a workaround.
6. Continuous Monitoring Risks evolve. A component that was safe today might become vulnerable tomorrow. SCA tools continuously monitor dependencies and alert you to new threats.
Key Features of Modern SCA Tools
Different vendors offer different capabilities, but modern SCA solutions generally provide:
- Automated Dependency Discovery: Scans codebases, containers, and manifests for libraries.
- SBOM Generation: Standardized formats like CycloneDX or SPDX.
- Vulnerability Intelligence: Real-time updates from multiple sources.
- License Risk Management: Detailed reporting on license obligations.
- Policy Enforcement: Block builds that include high-risk components.
- CI/CD Integration: Works with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps, etc.
- Governance & Reporting: Dashboards, compliance reports, and audit trails.
Popular tools include Dependency-Track, Snyk, WhiteSource (Mend), Black Duck, OWASP Dependency-Check, FOSSA, and GitHub Dependabot.

Popular SCA Tools and Resources
Below is a curated list of well-known SCA tools, including open-source and commercial options:
- Dependency-Track — open-source platform for managing SBOMs and tracking vulnerabilities.
- Snyk — developer-first SCA with rich integrations, CI/CD support, and automated remediation.
- WhiteSource (Mend) — enterprise-grade open-source risk management platform.
- Black Duck (Synopsys) — deep binary and source scanning for vulnerabilities and license compliance.
- OWASP Dependency-Check — an open-source tool for scanning known dependencies for vulnerabilities.
- FOSSA — focused on license compliance and vulnerability tracking.
- GitHub Dependabot / Advanced Security — integrates into GitHub ecosystems for dependency scanning.
- Google osv-scanner — an open-source SCA tool based on Google's osv.dev database.
- OSV-SCALIBR — Google's open-source Go library and scanner for SBOM generation and vulnerability detection.
- Aikido Security — modern SCA tool with dependency scanning, CI/CD integration, and secrets detection.
SCA vs SAST vs DAST: Where Does It Fit?
It's easy to confuse SCA with other security practices. Here's the distinction:
- SAST (Static Application Security Testing): Analyzes your proprietary source code for security flaws.
- DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing): Tests a running application from the outside, like a black-box scan.
- SCA (Software Composition Analysis): Focuses on third-party/open-source components in your code.
Together, they form a holistic application security strategy. Ignoring any of them leaves blind spots.

Challenges in Adopting SCA
While SCA is powerful, organizations often face hurdles:
- False Positives Some tools flag vulnerabilities even if the vulnerable function isn't used. This can overwhelm developers.
- Developer Resistance Developers may view SCA as a bottleneck slowing down delivery. Poorly integrated tools exacerbate this.
- Complex Dependency Trees Deeply nested transitive dependencies can be hard to patch or replace.
- Fragmented Tooling Organizations may struggle to choose between multiple tools, each with different strengths.
- Evolving Threat Landscape Vulnerability databases may lag behind real-world exploit discoveries.
The key is to integrate SCA thoughtfully into workflows and balance security with usability.

Best Practices for Effective SCA
To maximize the benefits of SCA, consider these best practices:
1. Shift Left Security
Run SCA scans early in the development process — not just in production. Integrate into IDEs and CI/CD pipelines so developers catch issues before code is merged.
2. Automate SBOM Generation
Automatically generate and maintain SBOMs for every build. This ensures traceability and simplifies compliance reporting.
3. Prioritize Critical Risks
Not every vulnerability is urgent. Focus on:
- CVEs with high CVSS scores.
- Components with known exploits.
- Dependencies in sensitive parts of your application.
4. Enforce Policies with Guardrails
Set rules like:
- Block builds with critical vulnerabilities.
- Disallow components with restrictive licenses.
- Mandate upgrades for outdated libraries.
5. Educate Developers
Train developers to understand SCA findings, licenses, and remediation workflows. Security awareness is just as important as tooling.
6. Continuous Monitoring
SCA isn't a one-time task. Continuously monitor dependencies for new vulnerabilities and apply patches promptly.
7. Combine with Other Security Practices
SCA should complement SAST, DAST, container security, and infrastructure scanning. A layered defense is always stronger.
Real-World Example: Log4Shell and SCA
When the Log4Shell vulnerability (CVE-2021–44228) hit, organizations scrambled to identify whether they were using affected versions of Log4j.
- Companies without SCA: Spent days manually grepping through codebases, searching dependency manifests, and chasing transitive dependencies.
- Companies with SCA: Ran a quick scan, generated an SBOM, and immediately flagged affected applications. Some tools even suggested the patched versions.
The difference was response speed, and in cybersecurity, speed is survival.
The Future of SCA
SCA is evolving beyond just vulnerability scanning. Emerging trends include:
- Deeper Contextual Analysis Tools will better analyze whether vulnerable functions are actually invoked, reducing false positives.
- Integration with AI/ML Predictive models to flag potentially risky components before CVEs are published.
- Expanded SBOM Adoption With government regulations (like the U.S. Executive Order on Cybersecurity), SBOMs are becoming mandatory in many industries.
- End-to-End Supply Chain Security SCA will merge with broader supply chain security practices, covering build systems, package registries, and CI/CD pipelines.

Conclusion
In today's hyper-connected software ecosystem, you can't secure what you don't understand. With open-source dependencies forming the backbone of modern applications, Software Composition Analysis (SCA) has become a non-negotiable part of application security.
SCA provides organizations with visibility into their dependencies, highlights vulnerabilities, ensures license compliance, and enables a rapid response to emerging threats. When integrated thoughtfully into the SDLC, it empowers developers to innovate confidently while keeping security and compliance in check.
PART II: Link will be updated soon.

Stay updated with our latest blogs, where we cover the newest trends in technology and cybersecurity. From emerging threats to innovative solutions, we bring you expert insights and analysis. Explore in-depth articles, tips, and updates tailored for tech enthusiasts and professionals. Don't miss out — check back regularly for fresh content!
