Introduction
In today's hyper connected digital landscape, understanding vulnerabilities, Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT), is essential for protecting systems from cyber threats. This module explores key vulnerabilities that compromise system integrity and the best practices to mitigate them.
Understanding Vulnerabilities
A vulnerability is a weakness in software, hardware, or network systems that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access, disrupt services, or steal data.

Key Concepts :
- Vulnerability Assessment: Identifies and prioritizes potential weaknesses in systems.
- Penetration Testing: Simulates real-world attacks by exploiting those vulnerabilities to assess system resilience.
- OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project): A non-profit organization providing widely adopted guidelines, tools, and resources for web application security.
Memory Injections and Buffer Overflow
Memory Injection :
Memory injection occurs when malicious code or data is inserted into a program's memory, causing unintended commands to execute. This often leads to privilege escalation or full system compromise.
Buffer Overflow :
A buffer overflow happens when excess data is written beyond the memory buffer's limit, overwriting adjacent memory. This can cause system crashes or enable execution of malicious code.
Both vulnerabilities stem from poor memory management and are common vectors for advanced cyber attacks.

Race Conditions
A race condition arises when a program's outcome depends on the timing or sequence of certain events — especially when multiple processes or threads access the same data simultaneously.
Real-World Examples :
- Two users attempting to withdraw funds from a bank account simultaneously.
- Multiple users buying the last item in stock at once.
- Traffic lights turning red and green simultaneously due to timing errors.
Prevention Techniques :
- Synchronization: Coordinate process execution to prevent conflicts.
- Locking: Restrict simultaneous access to shared resources.
- Atomic Operations: Execute actions as indivisible units to ensure data consistency.
Malicious Updates
Malicious updates occur when attackers compromise software updates, injecting harmful code into legitimate update packages.
Risks :
- Installation of malware or backdoors.
- System failure or data breaches.
- Unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Prevention :
Always verify update integrity and use secure distribution channels to ensure software authenticity.
OS Vulnerabilities
Operating System (OS) vulnerabilities are weaknesses within the OS that can be exploited for unauthorized access, privilege escalation, or system disruption.
Causes :
- Coding errors
- Misconfigurations
- Outdated software
- Design flaws
Examples :
- Unpatched security holes
- Weak default settings
- Flaws in core system services
Prevention :
Regularly update systems, apply patches promptly, and follow best practices for OS configuration and hardening.
SQL Injections
SQL Injection (SQLi) attacks occur when malicious SQL commands are inserted into database queries due to insufficient input validation.

Impact :
- Unauthorized data access or modification
- Authentication bypass
- Execution of administrative operations
Example :
Exploiting a vulnerable login form to access or alter sensitive database records.
Prevention :
Implement parameterized queries, prepared statements, and strict input validation to safeguard database interactions.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerabilities
XSS vulnerabilities arise when attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by others, often through unvalidated user input.
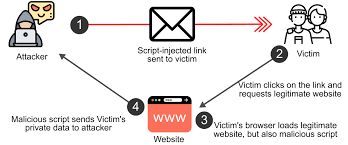
Example :
An attacker embeds JavaScript into a website's comment section to steal user cookies or hijack sessions.
Risks
- Session hijacking
- Data theft
- Unauthorized user actions
- Prevention
Use input validation, secure coding, and Content Security Policies (CSPs) to protect against XSS attacks.
Hardware Vulnerabilities
Hardware vulnerabilities stem from flaws in the design or manufacturing of physical components.
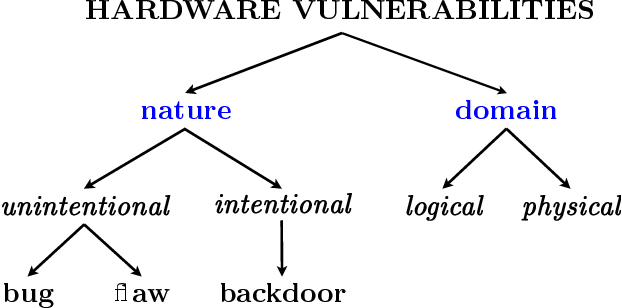
Examples :
- Processor flaws like Spectre and Meltdown, which expose sensitive data.
- Firmware vulnerabilities enabling unauthorized hardware control.
Challenges :
Hardware flaws are difficult to patch and often require firmware updates or hardware replacements.
Prevention :
Apply firmware upda tes regularly, ensure physical security, and leverage hardware-based security features.
Virtual Machine (VM) Vulnerabilities
VM vulnerabilities affect virtualized environments and can compromise both the host and other VMs.
Common Types :
- Hypervisor Vulnerabilities: Exploits that allow attackers to escape a VM and access the host system.
- VM Escape: Attackers execute code outside the VM boundary.
- Resource Contention: Exploiting shared resources like CPU or memory.
- Insecure Configuration: Weak isolation or poor access control.
Prevention :
Keep virtualization software updated, patch hypervisors, enforce strict VM isolation, and follow secure configuration practices.
Cloud Vulnerabilities
Cloud environments introduce new risks due to shared resources, APIs, and remote management.
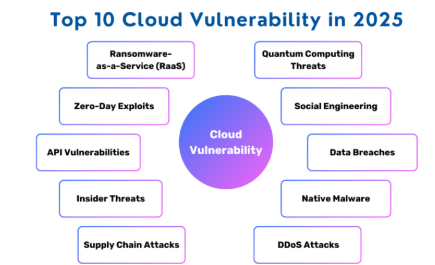
Common Vulnerabilities :
- Misconfigurations: Weak access controls or public data exposure.
- Data Breaches: Inadequate protection of stored or transmitted data.
- Insecure APIs: Poorly secured interfaces enabling exploitation.
- Account Hijacking: Credential theft leading to unauthorized access.
- Insufficient Security Controls: Lack of encryption, logging, and monitoring.
Mitigation Strategies :
- Proper configuration management
- Regular security assessments
- Strong access controls and encryption
- Continuous monitoring and auditing
Conclusion
Effective vulnerability management demands proactive identification, assessment, and mitigation of weaknesses across software, hardware, and cloud ecosystems. By adopting VAPT methodologies and OWASP standards, organizations can significantly reduce exposure to cyber threats and strengthen their overall security posture.
WHITE PANTHER :
Follow for More : https://www.instagram.com/intelithics.io/?igsh=dDZkZGVmMnRlaW12#
