Why stored XSS matters:
Stored (persistent) XSS happens when user input is saved on the server and later rendered in pages without proper encoding. That stored content can run in other user's browsers and lead to account compromise, session theft, or unwanted actions.

Where to look (common sinks in forms):
- Comment boxes and reviews.
- Profile fields (bio, display name).
- Support/feedback forms that keep entries.
- Forum threads.
- Any place that saves input to a database and displays it later.
Demonstration:
Recently I have found the stored XSS bug into a target website where I was able to add the JavaScript payloads into profile updating fields.
1. This is the Dashboard of the target website We can see that there is edit personal info option here
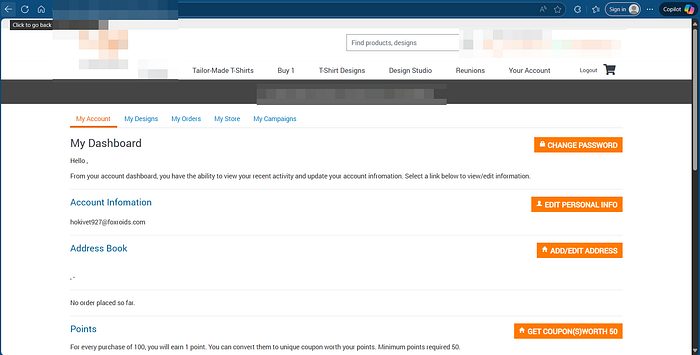
2. After clicking the Edit personal info, I opened a form where I could update first name, last name, additional email, phone number, etc.

3. I began by entering normal text into the input fields to observe the behavior.
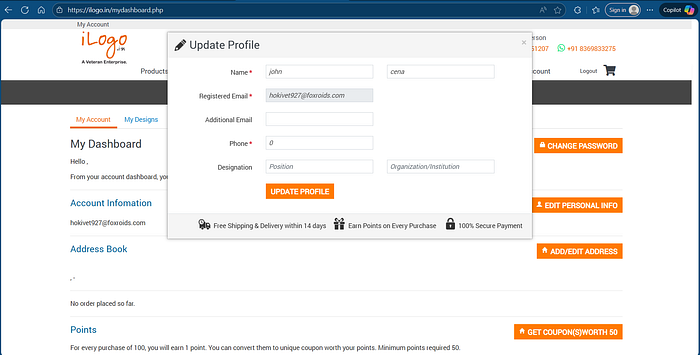
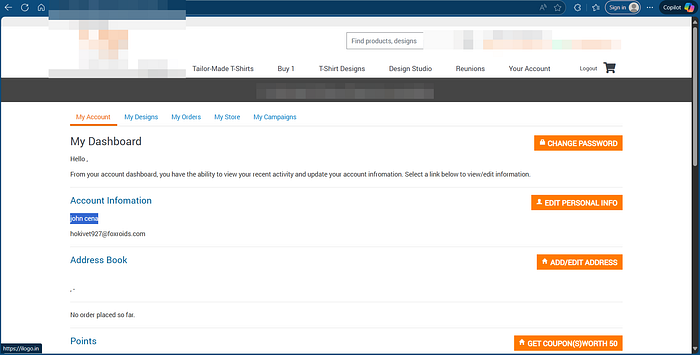
4. So After clicking the Update profile button, the profile was updated, and the new values were displayed on the name fields.
5. I used the browsers Inspect tool to see how the input was rendered. The input was being inserted inside a <p> tag.
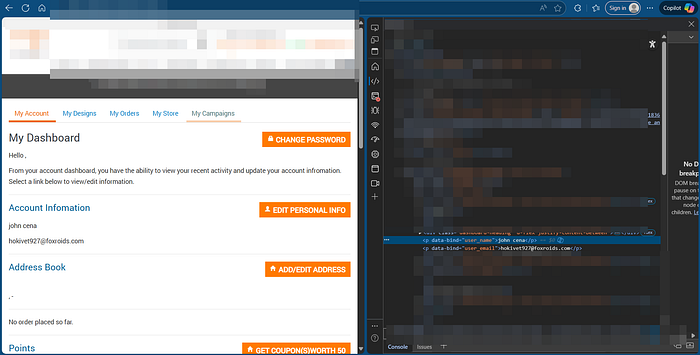
6. This context can be bypassed with simple payloads. While testing this target, entering a basic alert payload caused the dashboard layout collapse and part of the screen below the account information section became invisible, so I tested a polyglot payload.
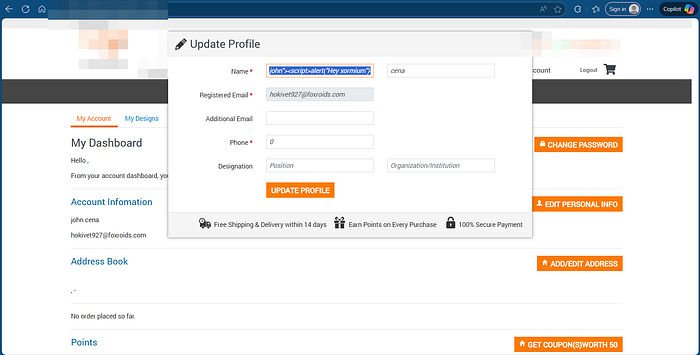
7. After adding the payload to the input, I received an alert popup on the screen, The alert triggered repeatedly when I logged back in and visited my profile page.
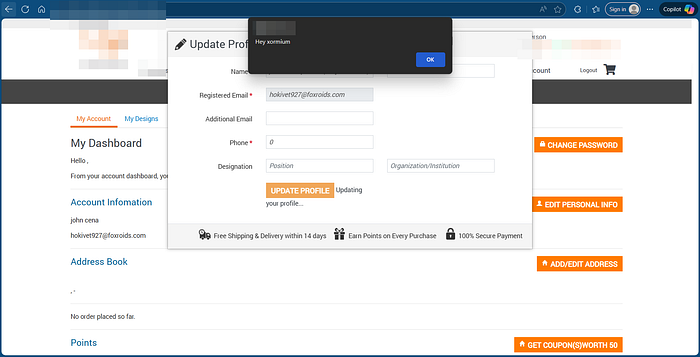
8. As since the site is an e-commerce platform, the popup also executed when I submitted a product review and when I added items to the cart and visited the cart page.
Remediation:
- Encode data at render time based on context like HTML body based (<, >, &).
- Use Content Security Policy (CSP).
- For comments or profiles, consider treating outputs as plain text by default.
Impact:
This could lead to session hijacking, credential theft, unauthorized actions on behalf of users, and phishing attacks. In an e-commerce website it may compromise user accounts, leak sensitive data, and damage brand trust.

